Temporal Changes in the Risk of Superspreading Events of Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 34322570
- PMCID: PMC8313518
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofab350
Temporal Changes in the Risk of Superspreading Events of Coronavirus Disease 2019
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Temporal Changes in the Risk of Superspreading Events of Coronavirus Disease 2019.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021 Nov 26;8(11):ofab432. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofab432. eCollection 2021 Nov. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34859111 Free PMC article.
Abstract
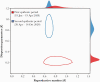
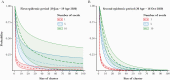
To identify the temporal change in the possible risk of superspreading events, we estimated the overdispersion parameter in 2 different periods of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. We determined that the possible risk of superspreading events was reduced 90% during the second epidemic period in South Korea.
Keywords: coronavirus; infectiousness; overdispersion; superspreading; transmission.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures