Triggering RNAi with multifunctional RNA nanoparticles and their delivery
- PMID: 34322586
- PMCID: PMC8315566
- DOI: 10.1515/rnan-2015-0001
Triggering RNAi with multifunctional RNA nanoparticles and their delivery
Abstract
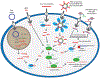
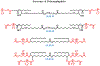
Proteins are considered to be the key players in structure, function, and metabolic regulation of our bodies. The mechanisms used in conventional therapies often rely on inhibition of proteins with small molecules, but another promising method to treat disease is by targeting the corresponding mRNAs. In 1998, Craig Mellow and Andrew Fire discovered dsRNA-mediated gene silencing via RNA interference or RNAi. This discovery introduced almost unlimited possibilities for new gene silencing methods, thus opening new doors to clinical medicine. RNAi is a biological process that inhibits gene expression by targeting the mRNA. RNAi-based therapeutics have several potential advantages (i) a priori ability to target any gene, (ii) relatively simple design process, (iii) site-specificity, (iv) potency, and (v) a potentially safe and selective knockdown of the targeted cells. However, the problem lies within the formulation and delivery of RNAi therapeutics including rapid excretion, instability in the bloodstream, poor cellular uptake, and inefficient intracellular release. In an attempt to solve these issues, different types of RNAi therapeutic delivery strategies including multifunctional RNA nanoparticles are being developed. In this mini-review, we will briefly describe some of the current approaches.
Keywords: RNA interference; RNA nanoparticles; RNA nanotechnology; RNA/DNA hybrids; delivery; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest
Figures
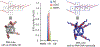

Similar articles
-
Theranostic Nanoparticles for RNA-Based Cancer Treatment.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Jun 18;52(6):1496-1506. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00101. Epub 2019 May 28. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31135134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing RNA interference to develop neonatal therapies: from Nobel Prize winning discovery to proof of concept clinical trials.Early Hum Dev. 2009 Oct;85(10 Suppl):S31-5. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2009.08.013. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Early Hum Dev. 2009. PMID: 19833462
-
RNAi-based therapeutics and tumor targeted delivery in cancer.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Mar;182:114113. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114113. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35063535 Review.
-
Efficient intracellular delivery and multiple-target gene silencing triggered by tripodal RNA based nanoparticles: a promising approach in liver-specific RNAi delivery.J Control Release. 2014 Dec 28;196:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Sep 20. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25251899
-
Green fluorescent protein specified small interfering RNA-cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles-Cy5.5.2008 Apr 17 [updated 2008 May 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Apr 17 [updated 2008 May 12]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641481 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Small-Angle Scattering as a Structural Probe for Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) in a Dynamic Solution Environment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 May 2;9(5):681. doi: 10.3390/nano9050681. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31052508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Picomolar Fingerprinting of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles Using Solid-State Nanopores.ACS Nano. 2017 Oct 24;11(10):9701-9710. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b04923. Epub 2017 Sep 11. ACS Nano. 2017. PMID: 28841287 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) as molecular tools to direct desirable and avoid undesirable immunological effects.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jun;173:427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.011. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33857556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges to optimizing RNA nanostructures for large scale production and controlled therapeutic properties.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2020 May 26;15(13):1331-40. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2020-0034. Online ahead of print. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32452262 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Behavior of RNA Nanoparticles Analyzed by AFM on a Mica/Air Interface.Langmuir. 2018 Dec 11;34(49):15099-15108. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00105. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Langmuir. 2018. PMID: 29669419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Social Security. http://www.ssa.gov/planners/lifeexpectancy.html (accessed March 6 2015).
-
- Soutschek J; Akinc A; Bramlage B; Charisse K; Constien R; Donoghue M; Elbashir S; Geick A; Hadwiger P; Harborth J, et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 173–178. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
