The RNA helicase Ddx52 functions as a growth switch in juvenile zebrafish
- PMID: 34323273
- PMCID: PMC8353168
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.199578
The RNA helicase Ddx52 functions as a growth switch in juvenile zebrafish
Abstract
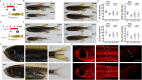
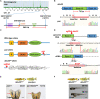
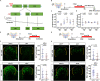
Vertebrate animals usually display robust growth trajectories during juvenile stages, and reversible suspension of this growth momentum by a single genetic determinant has not been reported. Here, we report a single genetic factor that is essential for juvenile growth in zebrafish. Using a forward genetic screen, we recovered a temperature-sensitive allele, pan (after Peter Pan), that suspends whole-organism growth at juvenile stages. Remarkably, even after growth is halted for a full 8-week period, pan mutants are able to resume a robust growth trajectory after release from the restrictive temperature, eventually growing into fertile adults without apparent adverse phenotypes. Positional cloning and complementation assays revealed that pan encodes a probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase (DEAD-Box Helicase 52; ddx52) that maintains the level of 47S precursor ribosomal RNA. Furthermore, genetic silencing of ddx52 and pharmacological inhibition of bulk RNA transcription similarly suspend the growth of flies, zebrafish and mice. Our findings reveal evidence that safe, reversible pauses of juvenile growth can be mediated by targeting the activity of a single gene, and that its pausing mechanism has high evolutionary conservation.
Keywords: ddx52; Forward genetics; RNA helicase; Regeneration; Zebrafish.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bennett, A. H., O'Donohue, M.-F., Gundry, S. R., Chan, A. T., Widrick, J., Draper, I., Chakraborty, A., Zhou, Y., Zon, L. I., Gleizes, P.-E.et al. (2018). RNA helicase, DDX27 regulates skeletal muscle growth and regeneration by modulation of translational processes. PLoS Genet. 14, e1007226. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007226 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bensimon-Brito, A., Cardeira, J., Dionísio, G., Huysseune, A., Cancela, M. L. and Witten, P. E. (2016). Revisiting in vivo staining with alizarin red S--a valuable approach to analyse zebrafish skeletal mineralization during development and regeneration. BMC Dev. Biol. 16, 2. 10.1186/s12861-016-0102-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouffard, S., Dambroise, E., Brombin, A., Lempereur, S., Hatin, I., Simion, M., Corre, R., Bourrat, F., Joly, J.-S. and Jamen, F. (2018). Fibrillarin is essential for S-phase progression and neuronal differentiation in zebrafish dorsal midbrain and retina. Dev. Biol. 437, 1-16. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.02.006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

