DNA methylation differences in cortical grey and white matter in schizophrenia
- PMID: 34323598
- PMCID: PMC8386513
- DOI: 10.2217/epi-2021-0077
DNA methylation differences in cortical grey and white matter in schizophrenia
Abstract
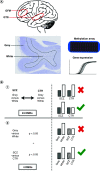
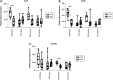
Aim: Identify grey- and white-matter-specific DNA-methylation differences between schizophrenia (SCZ) patients and controls in postmortem brain cortical tissue. Materials & methods: Grey and white matter were separated from postmortem brain tissue of the superior temporal and medial frontal gyrus from SCZ (n = 10) and control (n = 11) cases. Genome-wide DNA-methylation analysis was performed using the Infinium EPIC Methylation Array (Illumina, CA, USA). Results: Four differentially methylated regions associated with SCZ status and tissue type (grey vs white matter) were identified within or near KLF9, SFXN1, SPRED2 and ALS2CL genes. Gene-expression analysis showed differential expression of KLF9 and SFXN1 in SCZ. Conclusion: Our data show distinct differences in DNA methylation between grey and white matter that are unique to SCZ, providing new leads to unravel the pathogenesis of SCZ.
Keywords: DNA-methylation; postmortem; schizophrenia.
Plain language summary
Lay abstract This study investigated the way gene activity is regulated in brain cells of patients with schizophrenia (SCZ; a severe mental illness characterized by psychosis) compared with unaffected controls. The study focuses on the differences between parts of the brain with many cell bodies (grey matter) in contrast to those parts with mainly conducting fibers (white matter). For that purpose, grey and white matter were separated from brain tissue of ten individuals with SCZ and 11 without. All brains were obtained after the patients died and donated their brains to science. Array technology was used to analyze 800,000 sections of the DNA at once. The study identified regions on four genes that can turn the genes on and off differently in schizophrenic patients compared with controls, these genes were also turned on or off depending on their location either in grey or white matter. Two of these genes showed different activation in schizophrenic patients compared with controls. Overall this study identified distinct differences between grey and white matter that are unique to SCZ, providing new leads to unravel the biology of SCZ.
Conflict of interest statement
S Dracheva is supported by VA Merit grant I01BX002876 and by NIH/NIMH U01MH116442. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Olabi B, Ellison-Wright I, McIntosh A, Wood S, Bullmore E, Lawrie S. Are there progressive brain changes in schizophrenia? A meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies Biol. Psychiatry 70, 88–96 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wright I, Rabe-Hesketh S, Woodruff P, David A, Murray R, Bullmore E. Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 157, 16–25 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Cahn W, Van Haren NEM, Pol Het al.Brain volume changes in the first year of illness and 5-year outcome of schizophrenia. Br. J. Psychiatry 189, 381–382 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kyriakopoulos M, Vyas NS, Barker GJ, Chitnis XA, Frangou S. A diffusion tensor imaging study of white matter in early-onset schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 63(5), 519–523 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
