Efficacy and Safety of Seltorexant as Adjunctive Therapy in Major Depressive Disorder: A Phase 2b, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Adaptive Dose-Finding Study
- PMID: 34324636
- PMCID: PMC8653874
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyab050
Efficacy and Safety of Seltorexant as Adjunctive Therapy in Major Depressive Disorder: A Phase 2b, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Adaptive Dose-Finding Study
Abstract
Background: Seltorexant, a selective antagonist of human orexin-2 receptors, demonstrated antidepressant effects in a previous exploratory study in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD).
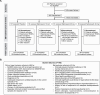
Methods: To replicate and extend this observation, a double-blind, adaptive dose-finding study was performed in patients with MDD who had an inadequate response to 1-3 selective serotonin/serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in the current episode. Patients were randomized (2:1:1) to placebo or seltorexant (20 mg or 40 mg) once-daily, administered adjunctively to the antidepressant the patient had been receiving at screening. After an interim analysis (6 weeks post-randomization of 160th patient), newly recruited patients randomly received (3:3:1) placebo or seltorexant 10 mg or 20 mg; the 40-mg dose was no longer assigned. Patients were stratified by baseline Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) scores (ISI ≥ 15 vs < 15). The primary endpoint was change from baseline Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) total score at week 6.
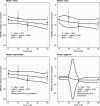
Results: Mixed-Model for Repeated Measures analysis showed a greater improvement in MADRS total score in the seltorexant 20-mg group vs placebo at weeks 3 and 6; least-square means difference (90% CI): -4.5 (-6.96; -2.07), P = .003; and -3.1 (-6.13; -0.16), P = .083, respectively. The improvement in MADRS score at week 6 for seltorexant 20 mg was greater in patients with baseline ISI ≥ 15 vs those with ISI < 15; least-square means difference (90% CI) vs placebo: -4.9 (-8.98; -0.80) and -0.7 (-5.16; 3.76), respectively. The most common (≥5%) adverse events with seltorexant were somnolence, headache, and nausea.
Conclusions: A clinically meaningful reduction of depressive symptoms was observed for seltorexant 20 mg. In the subset of patients with sleep disturbance (ISI ≥ 15), a larger treatment difference between seltorexant 20 mg and placebo was observed, warranting further investigation. No new safety signal was identified.
Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03227224.
Previous presentation: Poster presented at 58th Annual Meeting of American College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ACNP), December 8-11, 2019, Orlando, FL.
Keywords: Adjunctive therapy; major depressive disorder; orexin-2; seltorexant.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures


Comment in
-
Selective Orexin Receptor Antagonists as Novel Augmentation Treatments for Major Depressive Disorder: Evidence for Safety and Efficacy From a Phase 2B Study of Seltorexant.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022 Jan 12;25(1):85-88. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyab078. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34791262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauer M, Hefting N, Lindsten A, Josiassen MK, Hobart M (2019) A randomised, placebo-controlled 24-week study evaluating adjunctive brexpiprazole in patients with major depressive disorder. Acta Neuropsychiatr 31:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Bonaventure P, Shelton J, Yun S, Nepomuceno D, Sutton S, Aluisio L, Fraser I, Lord B, Shoblock J, Welty N, Chaplan SR, Aguilar Z, Halter R, Ndifor A, Koudriakova T, Rizzolio M, Letavic M, Carruthers NI, Lovenberg T, Dugovic C (2015) Characterization of JNJ-42847922, a selective orexin-2 receptor antagonist, as a clinical candidate for the treatment of insomnia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 354:471–482. - PubMed
-
- Brooks S, Jacobs GE, de Boer P, Kent JM, Van Nueten L, van Amerongen G, Zuiker R, Kezic I, Luthringer R, van der Ark P, van Gerven JM, Drevets W (2019) The selective orexin-2 receptor antagonist seltorexant improves sleep: an exploratory double-blind, placebo controlled, crossover study in antidepressant-treated major depressive disorder patients with persistent insomnia. J Psychopharmacol 33:202–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

