A new hybrid record linkage process to make epidemiological databases interoperable: application to the GEMO and GENEPSO studies involving BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers
- PMID: 34325649
- PMCID: PMC8320036
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-021-01299-6
A new hybrid record linkage process to make epidemiological databases interoperable: application to the GEMO and GENEPSO studies involving BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers
Abstract
Background: Linking independent sources of data describing the same individuals enable innovative epidemiological and health studies but require a robust record linkage approach. We describe a hybrid record linkage process to link databases from two independent ongoing French national studies, GEMO (Genetic Modifiers of BRCA1 and BRCA2), which focuses on the identification of genetic factors modifying cancer risk of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers, and GENEPSO (prospective cohort of BRCAx mutation carriers), which focuses on environmental and lifestyle risk factors.
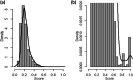
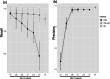
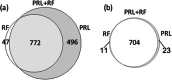
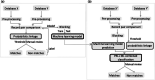
Methods: To identify as many as possible of the individuals participating in the two studies but not registered by a shared identifier, we combined probabilistic record linkage (PRL) and supervised machine learning (ML). This approach (named "PRL + ML") combined together the candidate matches identified by both approaches. We built the ML model using the gold standard on a first version of the two databases as a training dataset. This gold standard was obtained from PRL-derived matches verified by an exhaustive manual review. Results The Random Forest (RF) algorithm showed a highest recall (0.985) among six widely used ML algorithms: RF, Bagged trees, AdaBoost, Support Vector Machine, Neural Network. Therefore, RF was selected to build the ML model since our goal was to identify the maximum number of true matches. Our combined linkage PRL + ML showed a higher recall (range 0.988-0.992) than either PRL (range 0.916-0.991) or ML (0.981) alone. It identified 1995 individuals participating in both GEMO (6375 participants) and GENEPSO (4925 participants).
Conclusions: Our hybrid linkage process represents an efficient tool for linking GEMO and GENEPSO. It may be generalizable to other epidemiological studies involving other databases and registries.
Keywords: Hybrid process; Probabilistic linkage; Record linkage; Supervised machine learning.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Christen P, Goiser K. Quality and complexity measures for data linkage and deduplication. In: Guillet FJ, Hamilton HJ, editors. Quality measures in data mining. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2007. pp. 127–151.
-
- Fellegi IP, Sunter AB. A theory for record linkage. J Am Stat Assoc. 1969;64(328):1183–1210. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1969.10501049. - DOI
-
- Newcombe HB. Handbook of record linkage: methods for health and statistical studies, administration, and business. USA: Oxford University Press, Inc.; 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

