Diversity of inhibitory and excitatory parvalbumin interneuron circuits in the dorsal horn
- PMID: 34326298
- PMCID: PMC8832545
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002422
Diversity of inhibitory and excitatory parvalbumin interneuron circuits in the dorsal horn
Abstract
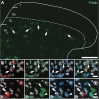
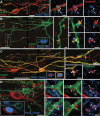
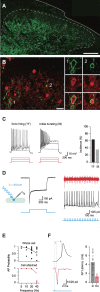
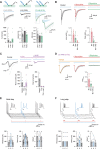
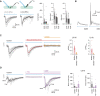
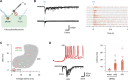
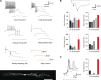
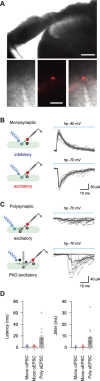
Parvalbumin-expressing interneurons (PVINs) in the spinal dorsal horn are found primarily in laminae II inner and III. Inhibitory PVINs play an important role in segregating innocuous tactile input from pain-processing circuits through presynaptic inhibition of myelinated low-threshold mechanoreceptors and postsynaptic inhibition of distinct spinal circuits. By comparison, relatively little is known of the role of excitatory PVINs (ePVINs) in sensory processing. Here, we use neuroanatomical and optogenetic approaches to show that ePVINs comprise a larger proportion of the PVIN population than previously reported and that both ePVIN and inhibitory PVIN populations form synaptic connections among (and between) themselves. We find that these cells contribute to neuronal networks that influence activity within several functionally distinct circuits and that aberrant activity of ePVINs under pathological conditions is well placed to contribute to the development of mechanical hypersensitivity.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Abraira VE, Kuehn ED, Chirila AM, Springel MW, Toliver AA, Zimmerman AL, Orefice LL, Boyle KA, Bai L, Song BJ, Bashista KA, O'Neill TG, Zhuo J, Tsan C, Hoynoski J, Rutlin M, Kus L, Niederkofler V, Watanabe M, Dymecki SM, Nelson SB, Heintz N, Hughes DI, Ginty DD. The cellular and synaptic architecture of the mechanosensory dorsal horn. Cell 2017;168:295–310.e19. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anelli R, Heckman CJ. The calcium binding proteins calbindin, parvalbumin, and calretinin have specific patterns of expression in the gray matter of cat spinal cord. J Neurocytol 2005;34:369–85. - PubMed
-
- Antal M, Freund TF, Polgár E. Calcium-binding proteins, parvalbumin- and calbindin-D 28k-immunoreactive neurons in the rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 1990;295:467–84. - PubMed
-
- Antal M, Polgár E, Chalmers J, Minson JB, Llewellyn-Smith I, Heizmann CW, Somogyi P. Different populations of parvalbumin- and calbindin-D28k-immunoreactive neurons contain GABA and accumulate 3H-D-aspartate in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 1991;314:114–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

