Cryo-EM structures of inhibitory antibodies complexed with arginase 1 provide insight into mechanism of action
- PMID: 34326456
- PMCID: PMC8322407
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02444-z
Cryo-EM structures of inhibitory antibodies complexed with arginase 1 provide insight into mechanism of action
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Cryo-EM structures of inhibitory antibodies complexed with arginase 1 provide insight into mechanism of action.Commun Biol. 2021 Nov 15;4(1):1310. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02832-5. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34782734 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
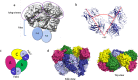
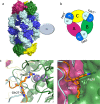
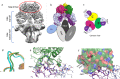
Human Arginase 1 (hArg1) is a metalloenzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of L-arginine to L-ornithine and urea, and modulates T-cell-mediated immune response. Arginase-targeted therapies have been pursued across several disease areas including immunology, oncology, nervous system dysfunction, and cardiovascular dysfunction and diseases. Currently, all published hArg1 inhibitors are small molecules usually less than 350 Da in size. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of potent and inhibitory anti-hArg antibodies bound to hArg1 which form distinct macromolecular complexes that are greater than 650 kDa. With local resolutions of 3.5 Å or better we unambiguously mapped epitopes and paratopes for all five antibodies and determined that the antibodies act through orthosteric and allosteric mechanisms. These hArg1:antibody complexes present an alternative mechanism to inhibit hArg1 activity and highlight the ability to utilize antibodies as probes in the discovery and development of peptide and small molecule inhibitors for enzymes in general.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Merck & Co., Inc., has filed provisional patent applications related to this paper. All authors are employees or former employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA and may hold stock or stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA.
Figures




References
-
- Bronte V, Serafini P, Apolloni E, Zanovello P. Tumor-induced immune dysfunctions caused by myeloid suppressor cells. J. Immunother. 2001;24:431–446. - PubMed
-
- Serafini P, Borrello I, Bronte V. Myeloid suppressor cells in cancer: recruitment, phenotype, properties and mechanisms of immune suppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006;16:53–65. - PubMed
-
- Bronte V, Serafini P, Mazzoni A, Segal DM, Zanovello P. L-arginine metabolism in myeloid cells controls T-lymphocyte functions. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:301–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

