Inflammatory effect on the gastrointestinal system associated with COVID-19
- PMID: 34326616
- PMCID: PMC8311540
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i26.4160
Inflammatory effect on the gastrointestinal system associated with COVID-19
Abstract
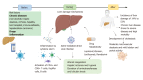
The severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) that causes coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) has provoked a global pandemic, mainly affecting the respiratory tract; however, a percentage of infected individuals can develop gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Some studies describe the development of GI symptoms and how they affect the progression of COVID-19. In this review, we summarize the main mechanisms associated with gut damage during infection by SARS-CoV-2 as well as other organs such as the liver and pancreas. Not only are host factors associated with severe COVID-19 but intestinal microbiota dysbiosis is also observed in patients with severe disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gastrointestinal symptoms; Gastrointestinal system; SARS-CoV-2.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest in publishing this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- National Institutes of Health. Coronaviruses. [cited 13 November 2020] Available from: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/coronaviruses .
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus disease. [cited 13 November 2020] Available from: https://covid19.who.int .
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Late sequelae of COVID-19. [cited 13 November 2020] Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/Late-sequela... .
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

