GlycA measured by NMR spectroscopy is associated with disease activity and cardiovascular disease risk in chronic inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 34327480
- PMCID: PMC8315361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2020.100120
GlycA measured by NMR spectroscopy is associated with disease activity and cardiovascular disease risk in chronic inflammatory diseases
Abstract
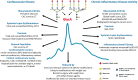
GlycA is a biomarker of systemic inflammation, quantifying both the protein concentrations and glycosylation states of several acute phase proteins. GlycA has been shown to be associated with both subclinical atherosclerosis and with cardiovascular disease (CVD). GlycA levels are higher in acute and chronic inflammation. During ongoing systemic inflammatory processes, GlycA specific acute phase reactants and proteins undergo circulating concentration and glycosylation pattern changes, and these alterations are reflected in the GlycA NMR signal. Additionally, levels associate with ongoing disease severity in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and psoriasis thus capturing active inflammation. Furthermore, in these disease states, GlycA is associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) independent of traditional risk factors including C-reactive protein (CRP). Finally, GlycA levels decrease with exercise, weight loss, and systemic anti-inflammatory agents. Therefore, GlycA appears to be a promising new composite biomarker of active systemic inflammation including assessing CVD risk in patients with inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Autoimmune disease; Cardiovascular disease risk; GlycA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Solomon D.H., Karlson E.W., Rimm E.B., Cannuscio C.C., Mandl L.A., Manson J.E. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation. 2003;107(9):1303–1307. - PubMed
-
- Avina-Zubieta J.A., Choi H.K., Sadatsafavi M., Etminan M., Esdaile J.M., Lacaille D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(12):1690–1697. - PubMed
-
- Meune C., Touze E., Trinquart L., Allanore Y. Trends in cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis over 50 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatology. 2009;48(10):1309–1313. - PubMed
-
- Meune C., Touze E., Trinquart L., Allanore Y. High risk of clinical cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis: levels of associations of myocardial infarction and stroke through a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archiv Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;103(4):253–261. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

