RadSimPE - a Radiology Workstation Simulator for Perceptual Education
- PMID: 34327629
- PMCID: PMC8455743
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-021-00489-4
RadSimPE - a Radiology Workstation Simulator for Perceptual Education
Abstract
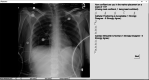
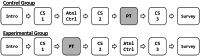
Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of simulation in radiology perceptual education. While current software exists for perceptual research, these software packages are not optimized for inclusion of educational materials and do not have full integration for presentation of educational materials. To address this need, we created a user-friendly software application, RadSimPE. RadSimPE simulates a radiology workstation, displays radiology cases for quantitative assessment, and incorporates educational materials in one seamless software package. RadSimPE provides simple customizability for a variety of educational scenarios and saves results to quantitatively document changes in performance. We performed two perceptual education studies involving evaluation of central venous catheters: one using RadSimPE and the second using conventional software. Subjects in each study were divided into control and experimental groups. Performance before and after perceptual education was compared. Improved ability to classify a catheter as adequately positioned was demonstrated only in the RadSimPE experimental group. Additional quantitative performance metrics were similar for both the group using conventional software and the group using RadSimPE. The study proctors felt that it was qualitatively easier to run the RadSimPE session due to integration of educational material into the simulation software. In summary, we created a user-friendly and customizable simulated radiology workstation software package for perceptual education. Our pilot test using the software for central venous catheter assessment was a success and demonstrated effectiveness of our software in improving trainee performance.
Keywords: Education; Perception; Python; Simulation; Software.
© 2021. Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Allerton D. Principles of flight simulation. John Wiley & Sons; 2009.
-
- Zyda M. From visual simulation to virtual reality to games. Computer. 2005;38(9):25–32. doi: 10.1109/MC.2005.297. - DOI
-
- Smith HM, Jacob AK, Segura LG, Dilger JA, Torsher LC. Simulation education in anesthesia training: a case report of successful resuscitation of bupivacaine-induced cardiac arrest linked to recent simulation training. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2008;106(5):1581–1584. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31816b9478. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

