Colloidal and vesicular delivery system for herbal bioactive constituents
- PMID: 34327650
- PMCID: PMC8602609
- DOI: 10.1007/s40199-021-00403-x
Colloidal and vesicular delivery system for herbal bioactive constituents
Abstract
Objectives: The main objective of the present review is to explore and examine the effectiveness of currently developed novel techniques to resolve the issues which are associated with the herbal constituents/extract.
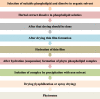
Methods: A systematic thorough search and collection of reviewed information from Science direct, PubMed and Google Scholar databases based on various sets of key phrases have been performed. All the findings from these data have been studied and briefed based on their relevant and irrelevant information.
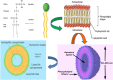
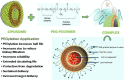
Result: Herbal drugs are gaining more popularity in the modern world due to their applications in curing various ailments with minimum toxic effects, side effect or adverse effect. However, various challenges exist with herbal extracts/plant actives such as poor solubility (water/lipid), poor permeation, lack of targeting specificity, instability in highly acidic pH, and liver metabolism, etc. Nowadays with the expansion in the technology, novel drug delivery system provides avenues and newer opportunity towards the delivery of herbal drugs with improved physical chemical properties, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic. Developing nano-strategies like Polymeric nanoparticles, Liposomes, Niosomes, Microspheres, Phytosomes, Nanoemulsion and Self Nano Emulsifying Drug Delivery System, etc. imparts benefits for delivery of phyto formulation and herbal bioactives. Nano formulation of phytoconstituents/ herbal extract could lead to enhancement of aqueous solubility, dissolution, bioavailability, stability, reduce toxicity, permeation, sustained delivery, protection from enzymatic degradation, etc. CONCLUSION: Based on the above findings, the conclusion can be drawn that the nano sized novel drug delivery systems of herbal and herbal bioactives have a potential future for upgrading the pharmacological action and defeating or overcoming the issues related with these constituents. The aims of the present review was to summarize and critically analyze the recent development of nano sized strategies for promising phytochemicals delivery systems along with their therapeutic applications supported by experimental evidence and discussing the opportunities for further aspects.
Keywords: Drug delivery system; Herbal medicine; Nano-strategies; Vesicular carriers.
© 2021. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Figures



References
-
- Ajazuddin SS. Applications of novel drug delivery system for herbal formulations. Fitoterapia. 2010;81:680–689. - PubMed
-
- Ajazuddin AA, Qureshi A, Kumari L, Vaishnav P, Sharma M, et al. Role of herbal bioactives as a potential bioavailability enhancer for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Fitoterapia. 2014;97:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Alexander A, Ajazuddin PRJ, Saraf S, Saraf S. Recent expansion of pharmaceutical nanotechnologies and targeting strategies in the field of phytopharmaceuticals for the delivery of herbal extracts and bioactives. J Control Release. 2016;241:110–124. - PubMed
-
- Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C. Christian Rrmesy LJ. Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:727–747. - PubMed
-
- Gupta M, Chauhan DN, Sharma V, Chauhan NS. Novel drug delivery systems for phytoconstituents. Nov Drug Deliv Syst Phytoconstituents. United States: CRC Press; 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

