A deep semantic segmentation correction network for multi-model tiny lesion areas detection
- PMID: 34330249
- PMCID: PMC8323231
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-021-01430-z
A deep semantic segmentation correction network for multi-model tiny lesion areas detection
Abstract
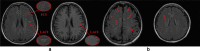
Background: Semantic segmentation of white matter hyperintensities related to focal cerebral ischemia (FCI) and lacunar infarction (LACI) is of significant importance for the automatic screening of tiny cerebral lesions and early prevention of LACI. However, existing studies on brain magnetic resonance imaging lesion segmentation focus on large lesions with obvious features, such as glioma and acute cerebral infarction. Owing to the multi-model tiny lesion areas of FCI and LACI, reliable and precise segmentation and/or detection of these lesion areas is still a significant challenge task.
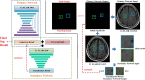
Methods: We propose a novel segmentation correction algorithm for estimating the lesion areas via segmentation and correction processes, in which we design two sub-models simultaneously: a segmentation network and a correction network. The segmentation network was first used to extract and segment diseased areas on T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images. Consequently, the correction network was used to classify these areas at the corresponding locations on T1 FLAIR images to distinguish between FCI and LACI. Finally, the results of the correction network were used to correct the segmentation results and achieve segmentation and recognition of the lesion areas.
Results: In our experiment on magnetic resonance images of 113 clinical patients, our method achieved a precision of 91.76% for detection and 92.89% for classification, indicating a powerful method to distinguish between small lesions, such as FCI and LACI.
Conclusions: Overall, we developed a complete method for segmentation and detection of WMHs related to FCI and LACI. The experimental results show that it has potential clinical application potential. In the future, we will collect more clinical data and test more types of tiny lesions at the same time.
Keywords: Focal cerebral ischemia; Lacunar infarct; Magnetic resonance imaging; Multi-modality; White matter hyperintensities.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lesion segmentation from multimodal MRI using random forest following ischemic stroke.Neuroimage. 2014 Sep;98:324-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.056. Epub 2014 May 2. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24793830
-
Improved Automatic Segmentation of White Matter Hyperintensities in MRI Based on Multilevel Lesion Features.Neuroinformatics. 2017 Jul;15(3):231-245. doi: 10.1007/s12021-017-9328-y. Neuroinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28378263
-
Automatic segmentation and quantitative analysis of white matter hyperintensities on FLAIR images using trimmed-likelihood estimator.Acad Radiol. 2014 Dec;21(12):1512-23. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Acad Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25176451
-
Automatic segmentation of cerebral white matter hyperintensities using only 3D FLAIR images.Magn Reson Imaging. 2013 Sep;31(7):1182-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.12.004. Epub 2013 May 16. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23684961
-
Extra tree forests for sub-acute ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in MR sequences.J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Jan 30;240:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.11.011. Epub 2014 Nov 21. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 25448384
Cited by
-
Context-aware augmentation for liver lesion segmentation: shape uniformity, expansion limit and fusion strategy.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Aug 1;13(8):5043-5057. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-1399. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37581084 Free PMC article.
-
Segmentation and differentiation of periventricular and deep white matter hyperintensities in 2D T2-FLAIR MRI based on a cascade U-net.Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1021477. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1021477. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36468062 Free PMC article.
-
A high-precision jujube disease spot detection based on SSD during the sorting process.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 5;19(1):e0296314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296314. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38180957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wardlaw JM, Pantoni L. Sporadic small vessel disease: pathogenic. Cereb Small Vessel Dis. 2014;52.
-
- Birenbaum A, Greenspan H. Longitudinal multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using multi-view convolutional neural networks. In: Deep learning and data labeling for medical applications, pp. 58–67. Springer, Cham; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 61872225/Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019-173/Introduction and Cultivation Program for Young Creative Talents in Colleges and Universities of Shandong Province
- ZR2015FM010/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (CN)
- ZR2019ZD04/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- J15LN20/Project of Science and technology plan of Shandong higher education institutions Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

