Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19
- PMID: 34330492
- PMCID: PMC8164501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011
Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19
Abstract
Background & aims: COVID-19 has emerged as a global pandemic affecting millions of people. Vitamin D deficiency is one of the risk factors for increased susceptibility to COVID-19. This study aimed to examine the correlation between the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 infection and mortality rates among the adult population in European and Asian continents.
Methods: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in each country was retrieved through literature searching on PubMed® database for the last ten years. As of December, 31st 2020, COVID-19 infections and mortalities per million population were extracted from the 'real time' statistics of the Worldometer website. The association between both vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 infections and mortalities were explored.
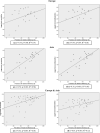
Results: Forty seven countries were included in the analysis. The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency ranged from 6.9 to 81.8% in European countries and 2.0-87.5% in Asian countries. Significantly positive correlations were observed for both COVID-19 infection (r = 0.76; p < 0.001) and mortality rates (r = 0.75; p < 0.001) in the Asian continent. The correlation values for the infections and mortality rates in the European continent were (r = 0.37; p = 0.08) and (r = 0.43; p = 0.04) respectively. When both the continents were combined, the correlation results for both infection (r = 0.42; p = 0.003) and mortality (r = 0.35; p = 0.016) rates with vitamin D deficiency values remained significant.
Conclusion: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was significantly associated with the mortality rate of COVID-19 in Europe and Asia. The association between the infection rate and prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was significant for Asia only. Both the associations were significant when the two continents were combined in the analysis. Therefore we suggest that vitamin D supplementation could play a key role in the prevention and/or treatment of the COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Asia; COVID-19; Deficiency; Europe; Infections; Mortalities; Vitamin D.
Copyright © 2021 European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Worldometer . 2021. COVID-19 coronovirus pandemic.https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ [updated January 28, 2021. Available from:
-
- Jin J., Agarwala N., Kundu P., Harvey B., Zhang Y., Wallace E., et al. medRxiv; 2020. Assessment of individual-and community-level risks for COVID-19 mortality in the US and implications for vaccine distribution.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials