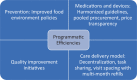
Blood from a stone: funding hypertension prevention, treatment, and care in low- and middle-income countries
- PMID: 34331004
- PMCID: PMC8654676
- DOI: 10.1038/s41371-021-00583-8
Blood from a stone: funding hypertension prevention, treatment, and care in low- and middle-income countries
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization and World Economic Forum. From burden to “best buys”: reducing the economic impact of non-communicable diseases in low and middle-income countries. Geneva: World Economic Forum; 2011.
-
- Geldsetzer P, Manne-Goehler J, Marcus M, Ebert C, Zhumadilov Z, Wesseh CS, et al. The state of hypertension care in 44 low-income and middle-income countries: a cross-sectional study of nationally representative individual-level data from 1·1 million adults. Lancet. 2019;394:652–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30955-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical