Isolation of Adult Mouse Cardiomyocytes Using Langendorff Perfusion Apparatus
- PMID: 34331252
- PMCID: PMC9801386
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1480-8_16
Isolation of Adult Mouse Cardiomyocytes Using Langendorff Perfusion Apparatus
Abstract
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death in the United States. Isolation and culture adult cardiomyocytes are important for studying cardiomyocyte contractility, heart hypertrophy, and cardiac failure. In contrast to neonatal cardiomyocyte isolation, adult mice cardiomyocytes isolation is challenging due to firm connections among cardiomyocytes through intercalated discs. The availability of newly generated genetically modified mouse lines requires to establish protocols to isolation and culture adult mouse cardiomyocyte for in vitro studies. In this manuscript, we described a straightforward method of isolating adult mouse cardiomyocytes using Langendorff perfusion apparatus. Briefly, the hearts were harvested from adult mice and the heart was mounted to Lagendorff apparatus. After perfusion with calcium depletion and collagenase digestion, the left ventricles were minced and filtered. Lastly, the separated cardiomyocytes were treated with CaCl2. The isolated cardiac myocytes can be utilized in a broad range of experiments including screening for drugs.
Keywords: Adult cardiomyocytes isolation; Langendorff; Trypsin.
© 2021. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
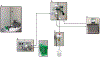
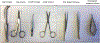
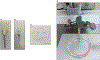


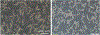
References
-
- Woodcock EA, Matkovich SJ (2005) Cardiomyocytes structure, function and associated pathologies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:1746–1751 - PubMed
-
- Powell T, Twist VW (1976) A rapid technique for the isolation and purification of adult cardiac muscle cells having respiratory control and a tolerance to calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 72:327–333 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

