Multiplexed Tissue Tomography
- PMID: 34331280
- PMCID: PMC8559895
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1593-5_6
Multiplexed Tissue Tomography
Abstract
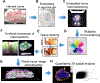
Multiplexed tissue tomography enables comprehensive spatial analysis of markers within a whole tissue or thick tissue section. Clearing agents are often used to make tissue transparent and facilitate deep tissue imaging. Many methods of clearing and tissue tomography are currently used in a variety of tissue types. Here we detail a workflow known as transparent tissue tomography (T3), which builds upon previous methods and can be applied to difficult to clear tissues such as tumors.
Keywords: Antibody; Immunofluorescence; Microscopy; Multiplex imaging; Tissue clearing; Tomography.
© 2021. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures


References
-
- Chung K, Wallace J, Kim S-Y, Kalyanasundaram S, Andalman AS, Davidson TJ, Mirzabekov JJ, Zalocusky KA, Mattis J, Denisin AK, Pak S, Bernstein H, Ramakrishnan C, Grosenick L, Gradinaru V, Deisseroth K (2013) Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature 497:332–337. doi: 10.1038/nature12107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

