CircRNAs as promising biomarker in diagnosis of breast cancer: An updated meta-analysis
- PMID: 34331339
- PMCID: PMC8418489
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23934
CircRNAs as promising biomarker in diagnosis of breast cancer: An updated meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been identified to be involved in onset and progression of multiple malignant tumors. The present study aimed to systematically evaluate the diagnostic values of circRNAs in breast cancer.
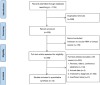
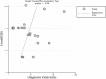
Methods: The PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, CNKI, and Wanfang online databases were searched for the relevant studies before December 31, 2020. Statistical analysis of the diagnostic tests was performed based on STATA 16.0, Meta-DiSc 1.4, and RevMan 5.3 software. The threshold effect and publication bias were measured by the Spearman correlation and Deeks' funnel plot asymmetry test, respectively.
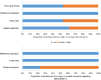
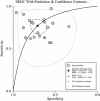
Results: Twenty-one studies from 13 articles were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.77 and 0.71, respectively. The pooled positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), and overall diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were 2.6, 0.33, and 8, respectively. Furthermore, the area under the summary receiver operator characteristic curve was 0.80. In addition, down-regulated circRNAs achieved a diagnostic performance higher than up-regulated circRNAs, with area under curve (AUC) values of 0.81 and 0.74, respectively. Studies based on tissue samples presented better diagnostic accuracy than those based on plasma samples, with AUC values of 0.80 and 0.67. In addition, two circRNAs, including circ_0001073 and circTADA2A-E5/E6, showed higher diagnostic values, with AUC value of 0.990 and 0.937, respectively. According to the results of meta-regression, the case size (p<0.05) might be the source of the heterogeneity.
Conclusion: CircRNAs exhibited a high diagnostic value for breast cancer and may function as potential diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer.
Keywords: biomarker; breast cancer; circular RNA; diagnosis; meta-analysis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of circRNAs in Esophageal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Dis Markers. 2019 Aug 27;2019:9673129. doi: 10.1155/2019/9673129. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31534563 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Dec;215(12):152680. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152680. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31635986
-
Long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1362437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38524131 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated circRNAs circ_0000745, circ_0001531 and circ_0001640 in human whole blood: Potential novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer.Exp Mol Pathol. 2021 Aug;121:104661. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104661. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Exp Mol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34139239
-
Abnormally Expressed Circular RNAs are Promising Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Meta-Analysis.Clin Lab. 2019 Nov 1;65(11). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190354. Clin Lab. 2019. PMID: 31710441
Cited by
-
Sevoflurane suppresses the malignant progression of breast cancer via the hsa_circ_0000129/miR-578/EPSTI1 axis.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Sep;14(26):2665-2677. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15053. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37533139 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0043278 inhibits breast cancer progression via the miR-455-3p/EI24 signalling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 20;21(1):1249. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08989-w. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34800978 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and diagnostic values of non-coding RNAs as biomarkers for breast cancer: An umbrella review and pan-cancer analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 16;10:1096524. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1096524. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36726376 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy using non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles for breast cancer management.Breast Cancer. 2025 Jan;32(1):16-25. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01562-w. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 38512533 Review.
-
Circ_0072088 promotes breast carcinoma progression via modulating miR-607/RNF2 axis.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Apr 15;16(4):1401-1414. doi: 10.62347/EONY6753. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38715837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Migowski A. Early detection of breast cancer and the interpretation of results of survival studies. Ciencia & Saude Coletiva. 2015;20(4):1309. - PubMed
-
- Coleman C. Early detection and screening for breast cancer. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2017;33(2):141‐155. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer A, Welch HG. Effect of three decades of screening mammography on breast‐cancer incidence. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367(21):1998‐2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

