Unbiased signal equation for quantitative magnetization transfer mapping in balanced steady-state free precession MRI
- PMID: 34331470
- PMCID: PMC8951070
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28940
Unbiased signal equation for quantitative magnetization transfer mapping in balanced steady-state free precession MRI
Abstract
Purpose: Quantitative magnetization transfer (qMT) imaging can be used to quantify the proportion of protons in a voxel attached to macromolecules. Here, we show that the original qMT balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) model is biased due to over-simplistic assumptions made in its derivation.
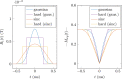
Theory and methods: We present an improved model for qMT bSSFP, which incorporates finite radiofrequency (RF) pulse effects as well as simultaneous exchange and relaxation. Furthermore, a correction relating to finite RF pulse effects for sinc-shaped excitations is derived. The new model is compared to the original one in numerical simulations of the Bloch-McConnell equations and in previously acquired in vivo data.
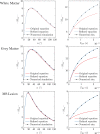
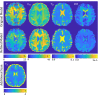
Results: Our numerical simulations show that the original signal equation is significantly biased in typical brain tissue structures (by 7%-20%), whereas the new signal equation outperforms the original one with minimal bias (<1%). It is further shown that the bias of the original model strongly affects the acquired qMT parameters in human brain structures, with differences in the clinically relevant parameter of pool-size-ratio of up to 31%. Particularly high biases of the original signal equation are expected in an MS lesion within diseased brain tissue (due to a low T2/T1-ratio), demanding a more accurate model for clinical applications.
Conclusion: The improved model for qMT bSSFP is recommended for accurate qMT parameter mapping in healthy and diseased brain tissue structures.
Keywords: balanced SSFP; magnetization transfer; quantitative imaging.
© 2021 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
P.J. is the Editor‐in‐Chief of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. In line with COPE guidelines, he recused himself from all involvement in the review process of this paper, which was handled by an Associate Editor. He and the other authors have no access to the identity of the reviewers.
Figures
References
-
- Gloor M, Scheffler K, Bieri O. Quantitative magnetization transfer imaging using balanced SSFP. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60:691‐700. - PubMed
-
- Gloor M, Scheffler K, Bieri O. Intrascanner and interscanner variability of magnetization transfer‐sensitized balanced steady‐state free precession imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65:1112‐1117. - PubMed
-
- Garcia M, Gloor M, Radue EW, et al. Fast high‐resolution brain imaging with balanced SSFP: interpretation of quantitative magnetization transfer towards simple MTR. NeuroImage. 2012;59:202‐211. - PubMed
-
- Bieri O, Scheffler K. SSFP signal with finite RF pulses. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62:1232‐1241. - PubMed
-
- Bieri O. An analytical description of balanced steady‐state free precession with finite radio‐frequency excitation. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65:422‐431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

