Epidemiological data and genome sequencing reveals that nosocomial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is underestimated and mostly mediated by a small number of highly infectious individuals
- PMID: 34332019
- PMCID: PMC8316632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.07.034
Epidemiological data and genome sequencing reveals that nosocomial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is underestimated and mostly mediated by a small number of highly infectious individuals
Abstract
Objectives: Despite robust efforts, patients and staff acquire SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospitals. We investigated whether whole-genome sequencing enhanced the epidemiological investigation of healthcare-associated SARS-CoV-2 acquisition.
Methods: From 17-November-2020 to 5-January-2021, 803 inpatients and 329 staff were diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection at four Oxfordshire hospitals. We classified cases using epidemiological definitions, looked for a potential source for each nosocomial infection, and evaluated genomic evidence supporting transmission.
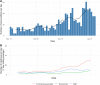
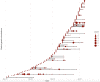
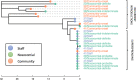
Results: Using national epidemiological definitions, 109/803(14%) inpatient infections were classified as definite/probable nosocomial, 615(77%) as community-acquired and 79(10%) as indeterminate. There was strong epidemiological evidence to support definite/probable cases as nosocomial. Many indeterminate cases were likely infected in hospital: 53/79(67%) had a prior-negative PCR and 75(95%) contact with a potential source. 89/615(11% of all 803 patients) with apparent community-onset had a recent hospital exposure. Within 764 samples sequenced 607 genomic clusters were identified (>1 SNP distinct). Only 43/607(7%) clusters contained evidence of onward transmission (subsequent cases within ≤ 1 SNP). 20/21 epidemiologically-identified outbreaks contained multiple genomic introductions. Most (80%) nosocomial acquisition occurred in rapid super-spreading events in settings with a mix of COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients.
Conclusions: Current surveillance definitions underestimate nosocomial acquisition. Most nosocomial transmission occurs from a relatively limited number of highly infectious individuals.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Nosocomial infection; SARS-CoV-2; Whole genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest DWE declares lecture fees from Gilead, outside the submitted work. No other author has a conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 variants with shortened incubation periods necessitate new definitions for nosocomial acquisition.J Infect. 2022 Feb;84(2):248-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.08.041. Epub 2021 Aug 30. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 34474059 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Discombe M. Covid infections caught in hospital rise by a third in one week n.d. https://www.hsj.co.uk/patient-safety/covid-infections-caught-in-hospital... (accessed May 20, 2021).
-
- Campbell D., Bawden A. Up to 8,700 patients died after catching Covid in English hospitals. Guardian. 2021 https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/may/24/up-to-8700-patients-died-a....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

