Intranasal vaccines for SARS-CoV-2: From challenges to potential in COVID-19 management
- PMID: 34332100
- PMCID: PMC8319039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.07.021
Intranasal vaccines for SARS-CoV-2: From challenges to potential in COVID-19 management
Abstract
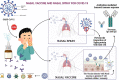
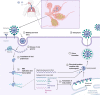
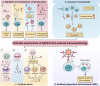
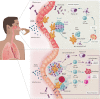
Unlike conventional Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines, intranasal vaccines display a superior advantage because the nasal mucosa is often the initial site of infection. Preclinical and clinical studies concerning intranasal immunization elicit high neutralizing antibody generation and mucosal IgA and T cell responses that avoid severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in both; the upper and lower respiratory tract. A nasal formulation is non-invasive with high appeal to patients. Intranasal vaccines enable self-administration and can be designed to survive at ambient temperatures, thereby simplifying logistical aspects of transport and storage. In this review, we provide an overview of nasal vaccines with a focus on formulation development as well as ongoing preclinical and clinical studies for SARS-CoV-2 intranasal vaccine products.
Keywords: Antigen-presenting cells (APCs); COVID-19; Dendritic cells; Nasal spray; Nasal vaccine; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral Bacteria Combined with an Intranasal Vaccine Protect from Influenza A Virus and SARS-CoV-2 Infection.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0159821. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01598-21. Epub 2021 Aug 17. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34399617 Free PMC article.
-
An Intranasal OMV-Based Vaccine Induces High Mucosal and Systemic Protecting Immunity Against a SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 17;12:781280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.781280. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34987509 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal COVID-19 vaccines: From bench to bed.EBioMedicine. 2022 Feb;76:103841. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103841. Epub 2022 Jan 24. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35085851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal administration of unadjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen boosts antigen-specific immune responses induced by parenteral protein subunit vaccine prime in mice and hamsters.Eur J Immunol. 2024 Jun;54(6):e2350620. doi: 10.1002/eji.202350620. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38561974
-
COVID-19 intranasal vaccines: current progress, advantages, prospects, and challenges.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2045853. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2045853. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35258416 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Remedies, Nutraceuticals, and Dietary Supplements for COVID-19 Management: An Update.Clin Complement Med Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;2(1):100021. doi: 10.1016/j.ccmp.2022.100021. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Clin Complement Med Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36620357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenic and reactogenic efficacy of Covaxin and Covishield: a comparative review.Immunol Res. 2022 Jun;70(3):289-315. doi: 10.1007/s12026-022-09265-0. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35192185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Selective SARS-CoV-2 Host-Directed Antiviral Targeting Stress Response to Reactive Oxygen Species.ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Jan 13;9(1):109-121. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c01243. eCollection 2023 Jan 25. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 36712488 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical Technology and Drug Delivery Design.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 10;15(7):1916. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071916. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Vector Vaccine Development and Application during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 18;10(7):1450. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071450. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bloomberg. Vaccine Tracker. www.bloomberg.com/graphics/covid-vaccine-tracker-global-distribution/ [accessed August 6, 2021].
-
- Zimmer C, Corum J, Wee S-L. Coronavirus vaccine tracker. NYTimes. www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/science/coronavirus-vaccine-tracker.html [accessed August 6, 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

