Short carboxyl terminal parathyroid hormone peptides modulate human parathyroid hormone signaling in mouse osteoblasts
- PMID: 34332324
- PMCID: PMC8380684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.085
Short carboxyl terminal parathyroid hormone peptides modulate human parathyroid hormone signaling in mouse osteoblasts
Abstract
Background: Novel human parathyroid hormone (hPTH) peptides of unknown biological activity have recently been identified in the serum of subjects with normal renal function, chronic renal failure, and end-stage renal disease through the application of liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry.
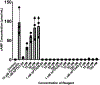
Purpose: of experiments: To determine the bioactivity of these peptides, we synthesized hPTH28-84, hPTH38-84, and hPTH45-84 peptides by solid phase peptide synthesis and tested their bioactivity in MC3T3-E1 mouse osteoblasts, either individually or together with the native hormone, hPTH1-84, by assessing the accumulation of 3´,5´-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and the induction of alkaline phosphatase activity.
Results: Increasing doses of hPTH1-84 (1-100 nM) increased the accumulation of cAMP and alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoblasts. hPTH28-84, hPTH38-84, and hPTH45-84 in concentrations of 1-100 nM were biologically inert. Surprisingly, 100 nM hPTH38-84 and hPTH45-84 increased the accumulation of cAMP in osteoblasts treated with increasing amounts of hPTH1-84. Human PTH28-84 had no effects on cAMP activity alone or in combination with hPTH1-84. Conversely, 100 nM hPTH38-84, hPTH45-84, and hPTH28-84 blocked the activation of alkaline phosphatase activity by hPTH1-84.
Conclusions: The data show that the short carboxyl-terminal hPTH peptides, hPTH38-84 and hPTH45-84, increase the amount of cellular cAMP generated in cultured osteoblasts in response to treatment with full-length hPTH1-84 when compared to full-length hPTH1-84 alone. Human PTH28-84 had no effect on cAMP activity alone or in combination with hPTH1-84. Human PTH28-84, hPTH38-84 and hPTH45-84 reduced the effects of hPTH1-84 in osteoblasts with respect to the induction of alkaline phosphatase activity compared to hPTH1-84 alone. Short carboxyl peptides of human PTH are biologically inert but when administered together with full-length hPTH1-84 modulate the bioactivity of hPTH1-84 in osteoblasts.
Keywords: Alkaline phosphatase; Carboxyl-terminal hPTH peptides; Mouse osteoblasts; cAMP; hPTH1-84; hPTH28-84; hPTH38-84; hPTH45-84.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None of the authors has any conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kritmetapak K, Losbanos LA, Hines JM, O’Grady KL, Ulmer CZ, Vesper HW, Enders FT, Singh RJ, Kumar R, Chemical Characterization and Quantification of Circulating Intact PTH and PTH Fragments by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry in Chronic Renal Failure, Clin Chem 67 (2021) 843–853. 10.1093/clinchem/hvab013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lopez MF, Rezai T, Sarracino DA, Prakash A, Krastins B, Athanas M, Singh RJ, Barnidge DR, Oran P, Borges C, Nelson RW, Selected reaction monitoring-mass spectrometric immunoassay responsive to parathyroid hormone and related variants, Clin Chem 56 (2010) 281–290. 10.1373/clinchem.2009.137323. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

