Usefulness of three-dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition MRI of large vessel occlusion for detecting occluded middle cerebral artery and internal carotid artery before acute mechanical thrombectomy
- PMID: 34332521
- PMCID: PMC8497723
- DOI: 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2020.10.007
Usefulness of three-dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition MRI of large vessel occlusion for detecting occluded middle cerebral artery and internal carotid artery before acute mechanical thrombectomy
Abstract
Objective: Acute mechanical thrombectomy (AMT) in patients with acute ischemic stroke from large vessel occlusion (LVO) is performed without directly identifying the occluded vessels. In this study, we evaluated whether 1.5 T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with 3D-fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA) could visualize the occluded intracranial middle cerebral artery (MCA) and internal carotid artery (ICA) before AMT.
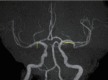
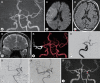
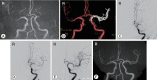
Methods: This retrospective study included 21 consecutive patients who underwent time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF MRA) and 3D-FIESTA MRI immediately before AMT. The patients also underwent TOF MRA after AMT and achieved TICI 2b or 3 by AMT at our hospital between February 2018 and April 2019. When LVO in the anterior circulation was detected by TOF MRA, 3D-FIESTA MRI was additionally performed. Then, the occluded intracranial MCA and ICA, including their branches, were constructed on the workstation with volume rendering. The obtained images were fused with the TOF MRA images to create combined 3D images.
Results: The length and top-to-bottom distance of the affected M1 segment (calculated by the ipsilateral-to-contralateral ratio) were 1.29 and 1.17, respectively, on 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT and 1.34 and 1.24, respectively, on TOF MRA after AMT. We assessed the number of M2 segments branching from the affected M1/M2 junction and visualized the affected anterior temporal artery. The 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT and TOF MRA after AMT were consistent in all patients, except for two who moved vigorously during imaging.
Conclusions: Images acquired by 1.5T 3D-FIESTA MRI can visualize to predict the existing path of the occluded MCA and ICA before AMT in patients with LVO of the anterior circulation.
Keywords: FIESTA; Large vessel occlusion; MRI; Mechanical thrombectomy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3D T2-Weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolutions (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-Flight (TOF) MR Angiography Fusion Imaging for Occluded Intracranial Arteries.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022;16(9):452-457. doi: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2021-0102. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 37502793 Free PMC article.
-
3D-FIESTA Magnetic Resonance Angiography Fusion Imaging of Distal Segment of Occluded Middle Cerebral Artery.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015;55(10):805-8. doi: 10.2176/nmc.tn.2014-0439. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 26369877 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Cerebral Large Vessel Occlusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke by MRI Positioning Scanning.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2021 Sep 15;61(9):521-527. doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2021-0028. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 34121049 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Occluded Distal Vessels with Variable Flip-Angle 3-Dimensional Turbo Spin-Echo Magnetic Resonance Imaging Before Acute Mechanical Thrombectomy.World Neurosurg. 2022 Nov;167:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.08.085. Epub 2022 Aug 24. World Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 36030009
-
Clinical Usefulness of Preoperative MCA Anatomical Scanning MRI in Thrombectomy Therapy for Acute Anterior Circulation Vessel Occlusion.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2021;15(7):421-428. doi: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2020-0118. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2021. PMID: 37502782 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
3D T2-Weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolutions (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-Flight (TOF) MR Angiography Fusion Imaging for Occluded Intracranial Arteries.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022;16(9):452-457. doi: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2021-0102. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 37502793 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial cerebrovascular lesions on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.J Clin Imaging Sci. 2024 Jun 19;14:19. doi: 10.25259/JCIS_16_2024. eCollection 2024. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2024. PMID: 38975060 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Occluded Middle Cerebral Artery Morphology for Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Contralateral Shape Analysis Approach.Asian J Neurosurg. 2024 Jun 24;19(3):435-438. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1787869. eCollection 2024 Sep. Asian J Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 39205893 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Mechanical Thrombectomy for Posterior Circulation Ischemia Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Arterial Structures.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2023 Mar 15;63(3):122-126. doi: 10.2176/jns-nmc.2022-0246. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2023. PMID: 36682792 Free PMC article.
-
Piecing Arterial Branching Pattern Together from Non-Contrast and Angiographic Brain Computed Tomography before Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 14;12(12):4051. doi: 10.3390/jcm12124051. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abanou A, Lasjaunias P, Manelfe C, Lopez-lbor L. The accessory middle cerebral artery (MCA). diagnostic and therapeutic consequences. Anat Clin. 1984;6(4):305–9. - PubMed
-
- Balami JS, White PM, McMeekin PJ, Ford GA, Buchan AM. Complication of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke: prevention and management. Int J Stroke. 2018 Jun;13(4):348–61. - PubMed
-
- Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jan;372(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- Blanc R, Pistocchi S, Babic D, Bartolini B, Obadia M, Alamowitch S, et al. Intravenous flat-detector CT angiography in acute ischemic stroke management. Neuroradiology. 2012 Apr;54(4):383–91. - PubMed

