Aggravation of functional mitral regurgitation on left ventricle stiffness in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients evaluated by CMR tissue tracking
- PMID: 34332579
- PMCID: PMC8325822
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01354-y
Aggravation of functional mitral regurgitation on left ventricle stiffness in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients evaluated by CMR tissue tracking
Abstract
Background: Functional mitral regurgitation (FMR) is one of the most common heart valve diseases in diabetes and may increase left ventricular (LV) preload and aggravate myocardial stiffness. This study aimed to investigate the aggravation of FMR on the deterioration of LV strain in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients and explore the independent indicators of LV peak strain (PS).
Materials and methods: In total, 157 T2DM patients (59 patients with and 98 without FMR) and 52 age- and sex-matched healthy control volunteers were included and underwent cardiac magnetic resonance examination. T2DM with FMR patients were divided into T2DM patients with mild (n = 21), moderate (n = 19) and severe (n = 19) regurgitation. LV function and global strain parameters were compared among groups. Multivariate analysis was used to identify the independent indicators of LV PS.
Results: The T2DM with FMR had lower LV strain parameters in radial, circumferential and longitudinal direction than both the normal and the T2DM without FMR (all P < 0.05). The mild had mainly decreased peak diastolic strain rate (PDSR) compared to the normal. The moderate had decreased peak systolic strain rate (PSSR) compared to the normal and PDSR compared to the mild and the normal. The severe FMR group had decreased PDSR and PSSR compared to the mild and the normal (all P < 0.05). Multiple linear regression showed that the regurgitation degree was independent associated with radial (β = - 0.272), circumferential (β = - 0.412) and longitudinal (β = - 0.347) PS; the months with diabetes was independently associated with radial (β = - 0.299) and longitudinal (β = - 0.347) PS in T2DM with FMR.
Conclusion: FMR may aggravate the deterioration of LV stiffness in T2DM patients, resulting in decline of LV strain and function. The regurgitation degree and months with diabetes were independently correlated with LV global PS in T2DM with FMR.
Keywords: Functional mitral regurgitation; Left ventricle; Magnetic resonance imaging; Strain; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
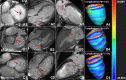
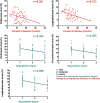
Similar articles
-
Additive effect of aortic regurgitation degree on left ventricular strain in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus evaluated via cardiac magnetic resonance tissue tracking.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Mar 11;21(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01471-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35277181 Free PMC article.
-
Atrioventricular coupling and left atrial abnormality in type 2 diabetes mellitus with functional mitral regurgitation patients verified by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jun 9;21(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01536-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35681217 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of subclinical LV myocardial dysfunction in T2DM patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jun 24;23(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02307-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38915040 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Mitral Valve Regurgitation, Pathophysiology, Leaflet ReModeling, and the Role of Imaging.Echocardiography. 2025 Mar;42(3):e70101. doi: 10.1111/echo.70101. Echocardiography. 2025. PMID: 39998385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular mechanics in individuals with mitral valve prolapse: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Aug;40(8):1617-1629. doi: 10.1007/s10554-024-03179-8. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38976111
Cited by
-
Additive Effects of Obesity on Myocardial Microcirculation and Left Ventricular Deformation in Essential Hypertension: A Contrast-Enhanced Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Mar 24;9:831231. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.831231. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35402539 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing right ventricular peak strain in myocardial infarction patients with mitral regurgitation by cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Apr 3;14(4):3018-3032. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1360. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38617148 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective UK Biobank study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Oct 29;21(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01663-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36309714 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking for Evaluating Myocardial Strain in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(8):98-109. doi: 10.2174/0115733998277127231211063107. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38310480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left-atrioventricular interaction and left-atrial deformation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with or without chronic aortic regurgitation: a 3.0-T cardiac magnetic resonance feature-tracking study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Apr 1;15(4):3198-3210. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-884. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40235815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15(7):539–553. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539::AID-DIA668>3.0.CO;2-S. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rossi A, Zoppini G, Benfari G, Geremia G, Bonapace S, Bonora E, Vassanelli C, Enriquez-Sarano M, Targher G. Mitral regurgitation and increased risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Med. 2017;130(1):70–76.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.07.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Faggiano P, Ciliberto R. L'insufficienza mitralica funzionale [Functional mitral insufficiency] Ital Heart J Suppl. 2000;1(10):1298–1303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

