Improvement in depressive symptoms after antiretroviral therapy initiation in people with HIV in Rakai, Uganda
- PMID: 34333739
- PMCID: PMC8524346
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-020-00920-6
Improvement in depressive symptoms after antiretroviral therapy initiation in people with HIV in Rakai, Uganda
Abstract
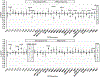
Depression is common following HIV infection and often improves after ART initiation. We aimed to identify distinct dimensions of depression that change following ART initiation in persons with HIV (PWH) with minimal comorbidities (e.g., illicit substance use) and no psychiatric medication use. We expected that dimensional changes in improvements in depression would differ across PWH. In an observational cohort in Rakai, Uganda, 312 PWH (51% male; mean age = 35.6 years) completed the Center for Epidemiologic Studies-Depression (CES-D) scale before and up to 2 years after ART initiation. Twenty-two percent were depressed (CES-D scores ≥ 16) pre-ART that decreased to 8% after ART. All CES-D items were used in a latent class analysis to identify subgroups with similar change phenotypes. Two improvement phenotypes were identified: affective-symptom improvement (n = 58, 19%) and mixed-symptom improvement (effort, appetite, irritability; n = 41, 13%). The affect-improvement subgroup improved on the greatest proportion of symptoms (76%). A third subgroup was classified as no-symptom changes (n = 213, 68%) as they showed no difference is symptom manifestation from baseline (93% did not meet depression criteria) to post-ART. Factors associated with subgroup membership in the adjusted regression analysis included pre-ART self-reported functional capacity, CD4 count, underweight BMI, hypertension, female sex(P's < 0.05). In a subset of PWH with CSF, subgroup differences were seen on Aβ-42, IL-13, and IL-12. Findings support that depression generally improves following ART initiation; however, when improvement is seen the patterns of symptom improvement differ across PWH. Further exploration of this heterogeneity and its biological underpinning is needed to evaluate potential therapeutic implications of these differences.
Keywords: Antiretroviral; Depression; Global health; HIV; Heterogeneity.
© 2021. Journal of NeuroVirology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest/Financial disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
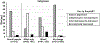

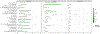
References
-
- Asrat B, Schneider M, Ambaw F, Lund C (2020). Effectiveness of psychological treatments for depressive symptoms among people living with HIV/AIDS in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 270: 174–187. - PubMed
-
- Bing EG, Burnam MA, Longshore D, Fleishman JA, Sherbourne CD, London AS, Turner BJ, Eggan F, Beckman R, Vitiello B, Morton SC, Orlando M, Bozzette SA, Ortiz-Barron L, Shapiro M (2001). Psychiatric disorders and drug use among human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults in the United States. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58: 721–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

