Therapeutic Effect of IL-4 Receptor-Targeting Pro-Apoptotic Peptide (AP1-ELP-KLAK) in Glioblastoma Tumor Model
- PMID: 34335025
- PMCID: PMC8318221
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S316388
Therapeutic Effect of IL-4 Receptor-Targeting Pro-Apoptotic Peptide (AP1-ELP-KLAK) in Glioblastoma Tumor Model
Abstract
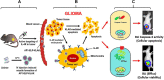
Background: Thermal-responsive self-assembled elastin-like polypeptide (ELP)-based nanoparticles are an emerging platform for controlled delivery of therapeutic peptides, proteins and small molecular drugs. The antitumor effect of bioengineered chimeric polypeptide AP1-ELP-KLAK containing an interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4R) targeting peptide and pro-apoptotic peptide (KLAKLAK) was evaluated in glioblastoma (GBM) in vitro and in vivo.
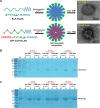
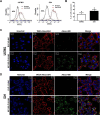
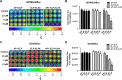
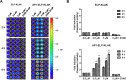
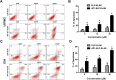
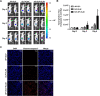
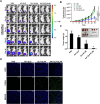
Methods and results: Herein, the therapeutic effect of AP1-ELP-KLAK was tested in advanced, and less curable glioblastoma cells with higher expression of IL-4R. Glioblastoma cell lines stably expressing different reporter systems i.e., caspase-3 sensor (surrogate marker for cellular apoptosis) or effluc/enhanced firefly luciferase (cellular viability) were established to measure cell death non-invasively. Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) of D54/effluc and U97MG/effluc treated with AP1-ELP-KLAK exhibited higher cell death up to 2~3-fold than the control. Treatment with AP1-ELP-KLAK resulted in time-dependent increase of caspase-3 sensor BLI activity in D54/C cells and D54/C tumor-bearing mice. Intravenous injection of AP1-ELP-KLAK dramatically reduced tumor growth by inducing cellular apoptosis in D54/effluc tumor-bearing mice. Further, the immuno-histological examination of the excised tumor tissue confirmed the presence of apoptotic cells as well as caspase-3 activation.
Conclusion: Collectively, AP1-ELP-KLAK effectively induced cellular apoptosis of glioblastoma cells and non-invasive imaging provides a window for real-time monitoring of anti-tumor effect with the provision of improving therapeutic efficacy in a glioblastoma mice model.
Keywords: ELP; IL-4 receptor; apoptosis; caspase-sensor; glioblastoma; tumor targeting.
© 2021 Sarangthem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

