Cardiovascular Effects Mediated by HMMR and CD44
- PMID: 34335086
- PMCID: PMC8286199
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/4977209
Cardiovascular Effects Mediated by HMMR and CD44
Abstract
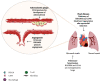
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. The most dangerous life-threatening symptoms of CVD are myocardial infarction and stroke. The causes of CVD are not entirely clear, and new therapeutic targets are still being sought. One of the factors involved in CVD development among vascular damage and oxidative stress is chronic inflammation. It is known that hyaluronic acid plays an important role in inflammation and is regulated by numerous stimuli, including proinflammatory cytokines. The main receptors for hyaluronic acid are CD44 and RHAMM. These receptors are membrane proteins that differ in structure, but it seems that they can perform similar or synergistic functions in many diseases. Both RHAMM and CD44 are involved in cell migration and wound healing. However, their close association with CVD is not fully understood. In this review, we describe the role of both receptors in CVD.
Copyright © 2021 Kinga Jaskuła et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

