Function of Uric Acid Transporters and Their Inhibitors in Hyperuricaemia
- PMID: 34335246
- PMCID: PMC8317579
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.667753
Function of Uric Acid Transporters and Their Inhibitors in Hyperuricaemia
Abstract
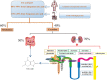
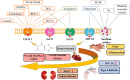
Disorders of uric acid metabolism may be associated with pathological processes in many diseases, including diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, and kidney disease. These diseases can further promote uric acid accumulation in the body, leading to a vicious cycle. Preliminary studies have proven many mechanisms such as oxidative stress, lipid metabolism disorders, and rennin angiotensin axis involving in the progression of hyperuricaemia-related diseases. However, there is still lack of effective clinical treatment for hyperuricaemia. According to previous research results, NPT1, NPT4, OAT1, OAT2, OAT3, OAT4, URAT1, GLUT9, ABCG2, PDZK1, these urate transports are closely related to serum uric acid level. Targeting at urate transporters and urate-lowering drugs can enhance our understanding of hyperuricaemia and hyperuricaemia-related diseases. This review may put forward essential references or cross references to be contributed to further elucidate traditional and novel urate-lowering drugs benefits as well as provides theoretical support for the scientific research on hyperuricemia and related diseases.
Keywords: gene; hyperuricaemia; inhibitor; transporters; uric acid.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Wu, Bian, Yang, Wang, Meng and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances on uric acid transporters.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 10;8(59):100852-100862. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20135. eCollection 2017 Nov 21. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29246027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insight into the management of renal excretion and hyperuricemia: Potential therapeutic strategies with natural bioactive compounds.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 22;13:1026246. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1026246. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36483739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urate Transporters in the Kidney: What Clinicians Need to Know.Electrolyte Blood Press. 2021 Jun;19(1):1-9. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2021.19.1.1. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2021. PMID: 34290818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uricosuric targets of tranilast.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017 Feb 6;5(2):e00291. doi: 10.1002/prp2.291. eCollection 2017 Apr. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017. PMID: 28357121 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of ABCG2 and other urate transporters in uric acid homeostasis in chronic kidney disease: potential role of remote sensing and signaling.Clin Kidney J. 2016 Jun;9(3):444-53. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfw010. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Clin Kidney J. 2016. PMID: 27274832 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Examining the Association of Rare Allelic Variants in Urate Transporters SLC22A11, SLC22A13, and SLC17A1 with Hyperuricemia and Gout.Dis Markers. 2024 Jan 6;2024:5930566. doi: 10.1155/2024/5930566. eCollection 2024. Dis Markers. 2024. PMID: 38222853 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility genes of hyperuricemia and gout.Hereditas. 2022 Aug 4;159(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00243-y. Hereditas. 2022. PMID: 35922835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of solute carrier proteins on disrupting substance regulation in metabolic disorders: insights and clinical applications.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 9;15:1510080. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1510080. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39850557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of METTL3 Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Upregulating ABCG2 m6A Modifications via IGF2BP2-Dependent Mechanisms in Hyperuricemic Nephropathy.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Mar;29(6):e70468. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70468. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40100069 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of single nucleotide polymorphisms affecting allopurinol pharmacokinetics and serum uric acid level.Pharmacogenomics. 2024;25(10-11):479-494. doi: 10.1080/14622416.2024.2403969. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Pharmacogenomics. 2024. PMID: 39347581
References
-
- Allen J. D., van Loevezijn A., Lakhai J. M., van der Valk M., van Tellingen O., Reid G., et al. (2002). Potent and Specific Inhibition of the Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Multidrug Transporter In Vitro and in Mouse Intestine by a Novel Analogue of Fumitremorgin C. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1, 417–425. - PubMed
-
- Anzai N., Miyazaki H., Noshiro R., Khamdang S., Chairoungdua A., Shin H. J., et al. (2004). The Multivalent PDZ Domain-Containing Protein PDZK1 Regulates Transport Activity of Renal Urate-Anion Exchanger URAT1 via its C Terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 45942–45950. 10.1074/jbc.M406724200 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

