Potential Regulatory Roles of GRK2 in Endothelial Cell Activity and Pathological Angiogenesis
- PMID: 34335610
- PMCID: PMC8320431
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.698424
Potential Regulatory Roles of GRK2 in Endothelial Cell Activity and Pathological Angiogenesis
Abstract
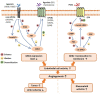
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinase 2 (GRK2) is an integrative node in many signaling network cascades. Emerging evidence indicates that GRK2 can interact with a large number of GPCRs and non-GPCR substrates in both kinase-dependent and -independent modes. Some of these pathways are associated with endothelial cell (EC) activity. The active state of ECs is a pivotal factor in angiogenesis. The occurrence and development of some inflammation-related diseases are accompanied by pathological angiogenesis, but there remains a lack of effective targeted treatments. Alterations in the expression and/or localization of GRK2 have been identified in several types of diseases and have been demonstrated to regulate the angiogenesis process in these diseases. GRK2 as a target may be a promising candidate for anti-angiogenesis therapy.
Keywords: GPCRs; GRK2; activity; angiogenesis; endothelial cells.
Copyright © 2021 Kuai, Han and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

