Influence of Systemic Administration of Coq10 Nanoparticles on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury on Ovaries in Rat
- PMID: 34335800
- PMCID: PMC8324357
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2303417
Influence of Systemic Administration of Coq10 Nanoparticles on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury on Ovaries in Rat
Abstract
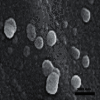
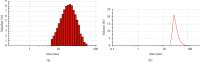
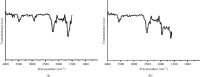
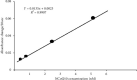
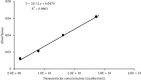
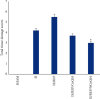
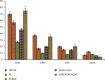
Using a rat ovary model, effects of COQ10 nanoparticles (NCOQ10) were studied on ischemia-reperfusion injury. In the present experimental study, following randomization of thirty healthy female Wistar rats ∼250 g, the animals were subjected to five experimental groups (n = 6): group SHAM : only laparotomy was performed, group IS: only a 3-hour ischemia was performed, group IS/REP: the procedure included a 3-hour ischemia followed by a 3-hour reperfusion, and 50 µL soybean oil (solvent of NCOQ10) was administered 30 min before cessation of reperfusion, group IS/NCOQ10: the procedure included a 3-hour ischemia only and 50 µL (0.3 mmol/lit/IP) of NCOQ10 30 min before cessation of ischemia, and group IS/REP/NCOQ10: the procedure included a 3-hour ischemia, a 3-hour reperfusion, and 20 µL (0.3 mmol/lit) of NCOQ10 30 min before cessation of ischemia. Significantly amended development of ischemia/reperfusion tissue injury was observed in animals treated with NCOQ10 compared to those of other groups (P=0.001). Mean values of biochemical indices were significantly higher than those observed for other groups (P=0.001). Significantly lower values of MDA were observed in IS/REP/NCOQ10 animals compared to those of other groups (P=0.001).Where ovarian tissue is exposed to ischemia, intraperitoneal administration of NCOQ10 could bear clinical benefits in diminishing ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Copyright © 2021 Pouria Honardoust et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Chang S.-H., Liu J.-Y., Hsiao M.-W., Yang H. L., Wang G.-W., Ye J.-C. Protective effects of Ocimum gratissimumAqueous extracts on HaCaT cells against UVC-induced inhibition of cell viability and migration. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 2021;18(9):2086–2092. doi: 10.7150/ijms.54644. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

