Tongxinluo Capsule Combined with Atorvastatin for Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34335841
- PMCID: PMC8313336
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9413704
Tongxinluo Capsule Combined with Atorvastatin for Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a common clinical cardiovascular disease, and its morbidity and mortality rates are increasing, which brings a serious burden to the family and society. Dyslipidemia is one of the most important risk factors for CHD. However, it is difficult to reduce blood lipids to an ideal state with the administration of a statin alone. Tongxinluo capsule (TXLC), as a Chinese patent medicine, has received extensive attention in the treatment of CHD in recent years. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to provide evidence-based medicine for TXLC combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of CHD.
Objective: To evaluate systematically the effectiveness and safety of TXLC combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of CHD.
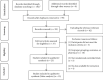
Methods: Seven English and Chinese electronic databases (PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, CNKI, VIP, CBM, and Wanfang) were searched from inception to January 2020, to search for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on TXLC combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of CHD. Two researchers independently screened the literature according to the literature inclusion and exclusion criteria and performed quality assessment and data extraction on the included RCTs. We performed a systematic review following Cochrane Collaboration Handbook and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and using a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews (AMSTAR 2). The quality of outcomes was evaluated by the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE). And meta-analysis was performed by Review Manager 5.2.
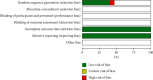
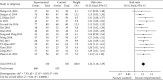
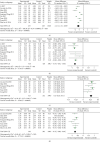
Results: A total of 15 RCTs with 1,578 participants were included in this review. Compared to atorvastatin treatment, TXLC combined with atorvastatin treatment showed potent efficacy when it came to the effectiveness of clinical treatment (RR = 1.24; 95% CI, 1.18, 1.29; P < 0.00001), total cholesterol (TC; MD = -1.21; 95% CI, -1.53, -0.89; P < 0.00001), triacylglycerol (TG; MD = -0.73; 95% CI, -0.81, -0.65; P < 0.00001), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C; MD = 0.27; 95% CI, 0.23, 0.31; P < 0.00001), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C; MD = -0.72; 95% CI, -0.80, -0.64; P < 0.00001), C-reactive protein (CRP; SMD = -2.06; 95% CI, -2.56, -1.57; P < 0.00001), frequency of angina pectoris (SMD = -1.41; 95% CI, -1.97, -0.85; P < 0.00001), duration of angina pectoris (MD = -2.30; 95% CI, -3.39, -1.21; P < 0.0001), and adverse reactions (RR = 0.84; 95% CI, 0.51, 1.39; P=0.50). No serious adverse events or reactions were mentioned in these RCTs. According to the PRISMA guidelines, although all studies were not fully reported in accordance with the checklist item, the reported items exceeded 80% of all items. With the AMSTAR 2 standard, the methodological quality assessment found that 9 studies were rated low quality and 6 studies were rated critically low quality. Based on the results of the systematic review, the GRADE system recommended ranking method was used to evaluate the quality of evidence and the recommendation level. The results showed that the level of evidence was low, and the recommendation intensity was a weak recommendation.
Conclusions: TXLC combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of CHD can effectively improve the effectiveness of clinical treatment, significantly reduce the frequency and duration of angina pectoris, decrease blood lipids, and improve inflammatory factors. However, due to the low quality of the literature included in these studies and the variability of the evaluation methods of each study, there is still a need for a more high-quality, large sample, multicenter clinical randomized control for further demonstration.
Copyright © 2021 Qiao Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ong P., Aziz A., Hansen H. S., et al. Structural and functional coronary artery abnormalities in patients with vasospastic angina pectoris. Circulation Journal. 2015;79(7):1431–1438. - PubMed
-
- Stewart R. A. H., Colquhoun D. M., Marschner S. L., et al. Persistent psychological distress and mortality in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Heart. 2017;103(23):1860–1866. - PubMed
-
- Chen H. Z., Lin G. W. Practical Internal Medicine. Beijing, China: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2009.
-
- Li R., Zhen Y., Xiao Y. P. Evaluation of the therapeutic effect and clinical safety of atorvastatin calcium combined with ezetimibe on coronary heart disease. Journal of Cardiopulmonary and Vascular Disease. 2016;35(4):266–268.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

