Effects of Enalapril on TLR2/NF- κ B Signaling Pathway and Inflammatory Factors in Rabbits with Chronic Heart Failure
- PMID: 34335842
- PMCID: PMC8294953
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9594607
Effects of Enalapril on TLR2/NF- κ B Signaling Pathway and Inflammatory Factors in Rabbits with Chronic Heart Failure
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Enalapril on TLR2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Inflammatory Factors in Rabbits with Chronic Heart Failure.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9828760. doi: 10.1155/2023/9828760. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125177 Free PMC article.
Abstract
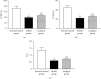
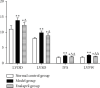
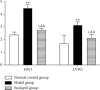
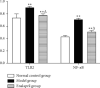
Chronic heart failure (CHF) refers to the state of persistent heart failure, which is a complex clinical syndrome of various advanced heart diseases. The toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2)/nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB) signal transduction pathway is one of the pathological mechanisms of CHF. Adriamycin can significantly induce the upregulation of TLR2 expression. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) are commonly used drugs for the treatment of CHF. In our study, the CHF model was established by injection of doxorubicin into the rabbit ear vein. The effect of enalapril on the TLR2/NF-κB signaling pathway in CHF rabbits has been analyzed and determined. Our research results showed that enalapril reduced the inflammatory response by inhibiting the activation of the TLR2/NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby improving cardiac structure, myocardial remodeling, and cardiac function.
Copyright © 2021 Yanping Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-30a-5p Promotes Chronic Heart Failure in Rats by Targeting Sirtuin-1 to Activate the Nuclear Factor-κB/NOD-Like Receptor 3 Signaling Pathway.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023 Dec;37(6):1065-1076. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07304-w. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023. PMID: 35488974 Review.
-
Non-Esterified Fatty Acids Over-Activate the TLR2/4-NF-Κb Signaling Pathway to Increase Inflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Neutrophils from Ketotic Cows.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(2):827-837. doi: 10.1159/000491913. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30032133
-
Roles of lipoxin A4 receptor activation and anti-interleukin-1β antibody on the toll-like receptor 2/mycloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB pathway in airway inflammation induced by ovalbumin.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):895-904. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3443. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25760938 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA NEAT1 alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by regulating the TLR2/NF-κB signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;23(11):4898-4907. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18078. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31210324
-
Efficacy of Sishen Wan on dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis and its effect on toll-like receptor 2/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2022 Aug;42(4):565-575. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220608.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35848973 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TLR4-A Pertinent Player in Radiation-Induced Heart Disease?Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;14(5):1002. doi: 10.3390/genes14051002. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-inflammatory Effect of Chitosan Oligosaccharide on Heart Failure in Mice.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Oct 5;2022:8746530. doi: 10.1155/2022/8746530. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9816307. doi: 10.1155/2024/9816307. PMID: 36246979 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Role of oxidative stress and inflammation-related signaling pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar 14;21(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01077-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36918950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Seq analysis of human heart tissue reveals SARS-CoV-2 infection and inappropriate activation of the TNF-NF-κB pathway in cardiomyocytes.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69635-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333655 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Effects of Enalapril on TLR2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Inflammatory Factors in Rabbits with Chronic Heart Failure.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9828760. doi: 10.1155/2023/9828760. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu M., Ye L., Bian J., Ma L., Zheng C., Guo H. Effect of Jiawei Shenfu decoction on tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nuclear factor-kappa B in patients who have chronic heart failure with syndromes of deficiency of heart Yang. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine = Chung I Tsa Chih Ying Wen pan. 2019;39(3):418–424. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

