Regulation of Mild Moxibustion on Uterine Vascular and Prostaglandin Contents in Primary Dysmenorrhea Rat Model
- PMID: 34335847
- PMCID: PMC8286201
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9949642
Regulation of Mild Moxibustion on Uterine Vascular and Prostaglandin Contents in Primary Dysmenorrhea Rat Model
Abstract
Objective: Primary dysmenorrhea (PD) is a common and high incidence disease in gynecology, which seriously affects the quality of life in young women. Our previous study found that mild moxibustion could treat abdominal pain of PD patients, but the mechanism is still unclear. Therefore, this study aims to partly investigate the treatment mechanism of moxibustion for PD, especially on uterine microcirculation.
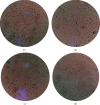
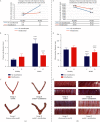
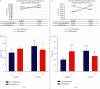
Methods: Forty 3-month-old Sprague Dawley female rats were randomly divided into four groups, including group A (saline control group, n = 10), group B (control plus moxibustion group, n = 10), group C (PD model group, n = 10), group D (PD. model plus moxibustion group, n = 10). The PD rat model was established by injecting estradiol benzoate and oxytocin. Mild moxibustion on Sanyinjiao (SP6) and Guanyuan (CV4) acupoints was once a day, 20 minutes per time, for 10 consecutive days. A vaginal smear was used to test the estrous cycle of rats. Uterine microvascular thickness was observed by stereomicroscope. And we detected the content of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α ) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in uterine tissue by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results: Mild moxibustion can enlarge the microvessels, improve the microcirculation disturbance, and relieve the swelling of the uterus in PD rats. During the mild moxibustion intervention, the contents of PGF2α and PGE2 in uterus issues were synchronous increases or decreases and the changes of PGE2 were more obvious, but the changes of uterine microvasculature and morphology caused by the decrease of PGF2α were greater than PGE2.
Conclusion: Mild moxibustion at SP6 and CV4 acupoints may relax uterine microvascular obstacle by reducing the content of PGF2α in uterine tissue, improve the microcirculation disorder, and then alleviate the PD rat's uterine swelling.
Copyright © 2021 Xuemei Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Herbal-cake-partitioned moxibustion of "Shenque" (CV8) has a relative specific effect in relieving abdominal pain and in regulating neuroendocrine-immune network in primary dysmenorrhea rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Feb 25;44(2):120-4. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170811. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 30945488 Chinese.
-
Mechanisms of acupuncture for primary dysmenorrhea based on PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in rats.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Dec 25;48(12):1258-1265. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20230007. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 38146249 Chinese, English.
-
[Effect of proximal and distal acupoint catgut-embedding on uterus prostaglandin, serum IL-2 and splenic NK cell activity in primary dysmenorrhea rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Mar 25;46(3):221-5. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200618. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 33798295 Chinese.
-
Effects of moxibustion or acupoint therapy for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea: a meta-analysis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2014 Jul-Aug;20(4):33-42. Altern Ther Health Med. 2014. PMID: 25141361 Review.
-
Uterine blood supply as a main factor involved in the regulation of the estrous cycle--a new theory.Reprod Biol. 2002 Jul;2(2):93-114. Reprod Biol. 2002. PMID: 14666152 Review.
Cited by
-
Moxibustion for Primary Dysmenorrhea: An Adjuvant Therapy for Pain Relief.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 27;2022:6864195. doi: 10.1155/2022/6864195. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35126603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine treatment strategies for primary dysmenorrhea.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 2;16:1580051. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1580051. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40385355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of wet cupping in a rat model of primary dysmenorrhea.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2024 Nov-Dec;15(6):101047. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2024.101047. Epub 2024 Dec 9. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39657369 Free PMC article.
-
Management of dysmenorrhea through yoga: A narrative review.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 30;4:1107669. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1107669. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37063942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomas B., Magos A. Modern management of dysmenorrhoea. Trends in Urology, Gynaecology & Sexual Health. 2009;14(5):25–29. doi: 10.1002/tre.120. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

