New Therapeutic Insight into the Effect of Ma Huang Tang on Blood Pressure and Renal Dysfunction in the L-NAME-Induced Hypertension
- PMID: 34335852
- PMCID: PMC8294972
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9980429
New Therapeutic Insight into the Effect of Ma Huang Tang on Blood Pressure and Renal Dysfunction in the L-NAME-Induced Hypertension
Abstract
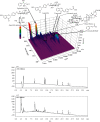
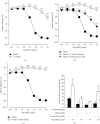
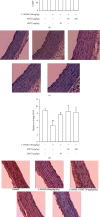
In this study, we evaluated the effect of a traditional herbal formula, Ma Huang Tang (MHT), on blood pressure and vasodilation in a rat model of NG-nitro-L-arginine methylester- (L-NAME-) induced hypertension. We found that MHT-induced vascular relaxation in a dose-dependent manner in rat aortas pretreated with phenylephrine. However, pretreatment of endothelium-intact aortic rings with L-NAME, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis (NOS), or 1H-[1, 2, 4]-oxadiazole-[4, 3-α]-quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ), an inhibitor of soluble guanylyl cyclase, significantly abolished vascular relaxation induced by MHT. MHT also increased the production of guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) in the aortic rings pretreated with L-NAME or ODQ. To examine the in vivo effects of MHT, Sprague Dawley rats were treated with 40 mg/kg/day L-NAME for 3 weeks, followed by administration of 50 or 100 mg/kg/day MHT for 2 weeks. MHT was found to significantly normalize systolic blood pressure and decreased intima-media thickness in aortic sections of rats treated with L-NAME compared to that of rats treated with L-NAME alone. MHT also restored the L-NAME-induced decrease in vasorelaxation response to acetylcholine and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) expression. Furthermore, MHT promoted the recovery of renal function, as indicated by osmolality, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, and creatinine clearance. These results suggest that MHT-induced relaxation in the thoracic aorta is associated with activation of the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway. Furthermore, it provides new therapeutic insights into the regulation of blood pressure and renal function in hypertensive patients.
Copyright © 2021 Mi Hyeon Hong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Daniel R. K., Kevin B., Carol M., Rebecca W., Jennifer L. L., Alan J. Impaired brachial artery endothelium-dependent and –independent vasodilation in men with erectile dysfunction and no other clinical cardiovascular disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2004;43:179–184. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

