Applicability and implementation of the collagen-induced arthritis mouse model, including protocols (Review)
- PMID: 34335888
- PMCID: PMC8290431
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10371
Applicability and implementation of the collagen-induced arthritis mouse model, including protocols (Review)
Abstract
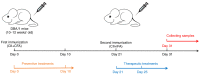
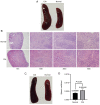
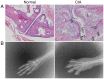
Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are essential for studying the pathogenesis of RA in vivo and determining the efficacy of anti-RA drugs. During the past decades, numerous rodent models of arthritis have been evaluated as potential models and the modeling methods are relatively well-developed. Among these models, the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model is the first choice and the most widely used because it may be generated rapidly and inexpensively and is relatively similar in pathogenesis to human RA. To date, there have been numerous classic studies and reviews discussing related pathogeneses and modeling methods. Based on this knowledge, combined with the latest convenient and effective methods for CIA model construction, the present review aims to introduce the model to beginners and clarify important details regarding its use. Information on the origin and pathogenesis of the CIA model, the protocol for establishing it, the rate of successful arthritis induction and the methods used to evaluate the severity of arthritis are briefly summarized. With this information, it is expected that researchers who have recently entered the field or are not familiar with this information will be able to start quickly, avoid unnecessary errors and obtain reliable results.
Keywords: applicability; collagen-induced arthritis; mouse model; protocol; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright: © Luan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
New Studies of Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Collagen-Induced and Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis Models: New Insight Involving Bacteria Flora.Autoimmune Dis. 2021 Mar 25;2021:7385106. doi: 10.1155/2021/7385106. eCollection 2021. Autoimmune Dis. 2021. PMID: 33833871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diallyl Trisulfide can induce fibroblast-like synovial apoptosis and has a therapeutic effect on collagen-induced arthritis in mice via blocking NF-κB and Wnt pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jun;71:132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.024. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30897500
-
Collagen-induced arthritis as a model of hyperalgesia: functional and cellular analysis of the analgesic actions of tumor necrosis factor blockade.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Dec;56(12):4015-23. doi: 10.1002/art.23063. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 18050216
-
Collagen-induced arthritis as an animal model for rheumatoid arthritis: focus on interferon-γ.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Dec;31(12):917-26. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0056. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21905879 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenolic-Compound-Rich Opuntia littoralis Ethyl Acetate Extract Relaxes Arthritic Symptoms in Collagen-Induced Mice Model via Bone Morphogenic Markers.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 17;14(24):5366. doi: 10.3390/nu14245366. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558525 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted PD-L1 alleviates inflammatory arthritis in mice through local and systemic AAV gene therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 3;16:1527858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1527858. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39963137 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA Promotes Synovial Proliferation and Bone Erosion in Rheumatoid Arthritis through Wnt/PCP Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Nov 1;2023:5057009. doi: 10.1155/2023/5057009. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 38022686 Free PMC article.
-
Short term, low dose alpha-ketoglutarate based polymeric nanoparticles with methotrexate reverse rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in mice and modulate T helper cell responses.Biomater Sci. 2022 Nov 22;10(23):6688-6697. doi: 10.1039/d2bm00415a. Biomater Sci. 2022. PMID: 36190458 Free PMC article.
-
Low Iron Diet Improves Clinical Arthritis in the Mouse Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Cells. 2024 Oct 29;13(21):1792. doi: 10.3390/cells13211792. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39513899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bird P, Kirkham B, Portek I, Shnier R, Joshua F, Edmonds J, Lassere M. Documenting damage progression in a two-year longitudinal study of rheumatoid arthritis patients with established disease (the DAMAGE study cohort): Is there an advantage in the use of magnetic resonance imaging as compared with plain radiography? Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1383–1389. doi: 10.1002/art.20165. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ejbjerg BJ, Vestergaard A, Jacobsen S, Thomsen HS, Østergaard M. The smallest detectable difference and sensitivity to change of magnetic resonance imaging and radiographic scoring of structural joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis finger, wrist, and toe joints: A comparison of the OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score applied to different joint combinations and the Sharp/van der Heijde radiographic score. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2300–2306. doi: 10.1002/art.21207. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
