Prognostic Value of KRAS Exon 3 and Exon 4 Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Patients
- PMID: 34335949
- PMCID: PMC8317521
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.59193
Prognostic Value of KRAS Exon 3 and Exon 4 Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Abstract
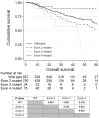
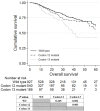
Background: The clinical significance of KRAS exon 3/4 mutations in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear. We aimed to assess the prognostic value of KRAS exons 3 and 4 mutations to determine the necessity for their testing. Methods: KRAS mutations in exon 2/3/4 were evaluated in 1816 stage I-IV patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma. Results: The mutation rates of KRAS and KRAS exons 2, 3, and 4 were 49.0%, 43.0%, 1.9%, and 4.1%, respectively. Univariate survival analysis showed that patients with exon 3 mutation had worse overall survival (OS) compared to those with KRAS exon 2 mutation or wild-type KRAS (P = 0.044, and P = 0.001). Meanwhile, there was no difference in survival between patients with wild-type KRAS and with exon 4 mutation (P = 0.128). In multivariate analysis, KRAS mutations in exon 3 and 2 were both independent factors for worse OS (Exon 3, P = 0.032, HR = 1.861, 95% CI: 1.021-3.391; Exon 2, P = 0.049, HR = 1.298, 95% CI: 1.002-1.682). Among the patients with KRAS exon 2 mutations, those that had mutations in codon 13 had significantly worse prognosis than those with wild-type KRAS (P = 0.001) or KRAS codon 12 mutations (P = 0.003). Conclusions: In KRAS-mutated CRC, exon 3 mutations predict the worst prognosis, while exon 4 mutations predict the best prognosis. Among KRAS exon 2 mutated patients, codon 13 mutations predict worse prognosis than codon 12 mutations. Mutations of different KRAS exons should be analyzed separately.
Keywords: KRAS exon 4; KRAS exon 3; KRAS mutations; clinicopathologic features; colorectal cancer; prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KRAS exon 2 codon 13 mutation is associated with a better prognosis than codon 12 mutation following lung metastasectomy in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2514-2524. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13697. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27911859 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS Exon 2 Mutations as Prognostic Indicators in Advanced Colorectal Cancer in Clinical Practice: A Mono-Institutional Study.Mol Diagn Ther. 2016 Feb;20(1):65-74. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0178-8. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26610798
-
Not all mutations of KRAS predict poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Mar 1;12(3):957-967. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31933906 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalent KRAS exon 2 c.35 G>A mutation in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: A biomarker of worse prognosis and potential benefit of bevacizumab-containing intensive regimens?Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015 Mar;93(3):190-202. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25459669 Review.
-
Prognostic and Predictive Value of RAS Gene Mutations in Colorectal Cancer: Moving Beyond KRAS Exon 2.Drugs. 2015 Oct;75(15):1739-56. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0459-x. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26347132 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations matter: An observational study of the prognostic and predictive value of KRAS mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 29;12:1055019. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1055019. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36523988 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of extended RAS/BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer with anti-EGFR antibody combinations.Pharmacogenomics. 2025 Jan-Feb;26(1-2):39-52. doi: 10.1080/14622416.2025.2479414. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Pharmacogenomics. 2025. PMID: 40097366 Review.
-
Multivariate Risk Analysis of RAS, BRAF and EGFR Mutations Allelic Frequency and Coexistence as Colorectal Cancer Predictive Biomarkers.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 4;14(11):2792. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112792. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681771 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Malignant Transformation of Tubulovillous Adenoma, Initially Presenting as McKittrick-Wheelock Syndrome: A Case Report.Case Rep Oncol. 2023 Sep 4;16(1):818-826. doi: 10.1159/000531992. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37900797 Free PMC article.
-
Association of various RAS codon mutations and prognostic outcomes of patients with colorectal liver metastases after hepatectomy.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(19):e70168. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70168. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39377605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA-CANCER J CLIN. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M. et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Lievre A, Bachet JB, Boige V, Cayre A, Le Corre D, Buc E. et al. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:374–9. - PubMed
-
- De Roock W, De Vriendt V, Normanno N, Ciardiello F, Tejpar S. KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, and PTEN mutations: implications for targeted therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:594–603. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M. et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1023–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous