Long-term live-cell lipid droplet-targeted biosensor development for nanoscopic tracking of lipid droplet-mitochondria contact sites
- PMID: 34335963
- PMCID: PMC8315056
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.59848
Long-term live-cell lipid droplet-targeted biosensor development for nanoscopic tracking of lipid droplet-mitochondria contact sites
Abstract
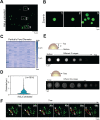
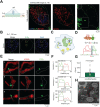
Background: Lipid droplets (LDs) establish a considerable number of contact sites with mitochondria to enable energy transfer and communication. In this study, we developed a fluorescent biosensor to image LD-mitochondria interactions at the nanoscale and further explored the function of LD-mediated matrix transmission in processes involving multi-organelle interactions. Methods: A fluorescent probe called C-Py (C21H19N3O2, 7-(diethylamino) coumarin-3-vinyl-4-pyridine acetonitrile) was designed and synthesized. Colocalization of C-Py and the commercial LD stain Nile Red was analyzed in HeLa cells. The fluorescence stability and signal to background ratio of C-Py under structured illumination microscopy (SIM) were compared to those of the commercial probe BODIPY493/503. The cytotoxicity of C-Py was assessed using CCK-8 assays. The uptake pattern of C-Py in HeLa cells was then observed under various temperatures, metabolic levels, and endocytosis levels. Contact sites between LDs and various organelles, such as mitochondria, nuclei, and cell membrane, were imaged and quantitated using SIM. Physical changes to the contact sites between LDs and mitochondria were monitored after lipopolysaccharide induction. Results: A LD-targeted fluorescent biosensor, C-Py, with good specificity, low background signal, excellent photostability, low cytotoxicity, and high cellular permeability was developed for tracking LD contact sites with multiple organelles using SIM. Using C-Py, the subcellular distribution and dynamic processes of LDs in living cells were observed under SIM. The formation of contact sites between LDs and multiple organelles was visualized at a resolution below ~200 nm. The number of LD-mitochondria contact sites formed was decreased by lipopolysaccharide treatment inducing an inflammatory environment. Conclusions: C-Py provides strategies for the design of ultra-highly selective biosensors and a new tool for investigating the role and regulation of LDs in living cells at the nanoscale.
Keywords: contact sites; extended-resolution imaging; lipid droplets; mitochondria.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

