MicroRNA-185-5p inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and reduces fasting blood glucose levels by suppressing G6Pase
- PMID: 34335967
- PMCID: PMC8315058
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.46882
MicroRNA-185-5p inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and reduces fasting blood glucose levels by suppressing G6Pase
Abstract
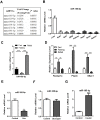
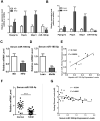
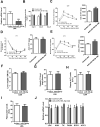
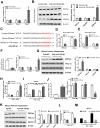
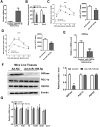
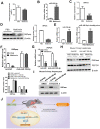
Aims/hypothesis: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known to contribute to many metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes. This study aimed to investigate the roles and molecular mechanisms of miR-185-5p in the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Methods: MicroRNA high-throughput sequencing was performed to identify differentially expressed miRNAs. High-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice and db/db mice, a genetic mouse model for diabetes, were used for examining the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR and Western blotting were performed to measure the expression levels of various genes and proteins. Luciferase reporter assays were used to determine the regulatory roles of miR-185-5p on G6Pase expression. Results: Hepatic miR-185-5p expression was significantly decreased during fasting or insulin resistance. Locked nucleic acid (LNA)-mediated suppression of miR-185-5p increased blood glucose and hepatic gluconeogenesis in healthy mice. In contrast, overexpression of miR-185-5p in db/db mice alleviated blood hyperglycemia and decreased gluconeogenesis. At the molecular level, miR-185-5p directly inhibited G6Pase expression by targeting its 3'-untranslated regions. Furthermore, metformin, an anti-diabetic drug, could upregulate miR-185-5p expression to suppress G6Pase, leading to hepatic gluconeogenesis inhibition. Conclusions/interpretation: Our findings provided a novel insight into the role of miR-185-5p that suppressed hepatic gluconeogenesis and alleviated hyperglycemia by targeting G6Pase. We further identified that the /G6Pase axis mediated the inhibitory effect of metformin on hepatic gluconeogenesis. Thus, miR-185-5p might be a therapeutic target for hepatic glucose overproduction and fasting hyperglycemia.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes; hepatic gluconeogenesis; hyperglycemia; metformin; miR-185-5p.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-451 Negatively Regulates Hepatic Glucose Production and Glucose Homeostasis by Targeting Glycerol Kinase-Mediated Gluconeogenesis.Diabetes. 2016 Nov;65(11):3276-3288. doi: 10.2337/db16-0166. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27495223
-
MicroRNA-21 regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by targeting FOXO1.Gene. 2017 Sep 5;627:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.024. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28627440
-
NFE2 Induces miR-423-5p to Promote Gluconeogenesis and Hyperglycemia by Repressing the Hepatic FAM3A-ATP-Akt Pathway.Diabetes. 2017 Jul;66(7):1819-1832. doi: 10.2337/db16-1172. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28411267
-
Recent advances of long non-coding RNAs in control of hepatic gluconeogenesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 31;14:1167592. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1167592. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37065737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Oct;13(10):572-587. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.80. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28731034 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Restoring gluconeogenesis by TEF inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis and immune surveillance in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Cancer Metab. 2023 Aug 8;11(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-023-00312-4. Cancer Metab. 2023. PMID: 37553601 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 6;7(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01073-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35794109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus murinus alleviates insulin resistance via promoting L-citrulline synthesis.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Apr;48(4):1005-1015. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02500-5. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 39560906
-
Potential role of microRNAs in selective hepatic insulin resistance: From paradox to the paradigm.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 21;13:1028846. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1028846. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36479211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;17(4):478. doi: 10.3390/ph17040478. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

