ATP-triggered mitochondrial cascade reactions for cancer therapy with nanoscale zeolitic imidazole framework-90
- PMID: 34335969
- PMCID: PMC8315074
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.59593
ATP-triggered mitochondrial cascade reactions for cancer therapy with nanoscale zeolitic imidazole framework-90
Abstract
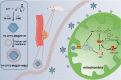
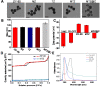
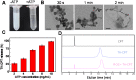
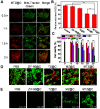
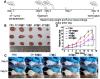
Goals: Chemotherapy, the most conventional modality for cancer therapy, usually brings serious side effects because of the low cancer-therapeutic specificity and bioavailability. It is of great significance for cancer treatment to develop new effective strategies to regulate biochemical reactions in organelles, enhance the specificity of chemotherapeutic drugs and reduce their side effects. Methods: We report herein a zeolitic imidazole framework-90 (ZIF-90) based nanoplatform, which was used to initiate a series of mitochondrial cascade reactions using ATP as a molecular switch for cancer therapy. The thioketal linked camptothecin (camptothecin prodrug, TK-CPT) and 2-Methoxyestradiol (2-ME) were encapsulated into the pores of ZIF-90 nanoparticles using a simple one-pot method, and the nanoplatform was finally coated with a layer of homologous cell membrane. Results: Mitochondrial ATP can efficiently degrade ZIF-90 and then release the loaded 2-ME and CPT prodrugs. 2-ME can inhibit the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), which induces the up-regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in situ. The thioketal linkers in CPT prodrug can respond to ROS, thereby achieving subsequent release of parent CPT drug. This cascade of reactions can lead to prolonged high oxidative stress and cause continuous cancer cell apoptosis, due to the increased ROS level and the liberation of CPT. Conclusion: We constructed an ATP-triggered strategy using nanoscale ZIF-90 to initiate mitochondrial cascade reactions for cancer therapy. The ZIF-90 based nanoplatform exhibited low cytotoxicity, good mitochondria-targeting ability, and excellent therapeutic effect. In vivo experiments demonstrated that the growth of tumor can be efficiently inhibited in a mouse model. This ATP-triggered strategy to induce mitochondrial biochemical reactions offers more possibilities for developing organelle-targeted therapeutic platforms.
Keywords: 2-methoxyestradiol; ATP; camptothecine; reactive oxygen species; zeolitic imidazole framework-90.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Li N, Sun Q, Yu Z, Gao X, Pan W, Wan X. et al. Nuclear-targeted photothermal therapy prevents cancer recurrence with near-infrared triggered copper sulfide nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2018;12:5197–206. - PubMed
-
- Seidi F, Jenjob R, Crespy D. Designing smart polymer conjugates for controlled release of payloads. Chem Rev. 2018;118:3965–4036. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Li T, Han F, Wang Y, Gan Y, Shi J. et al. A cascade-reaction enabled synergistic cancer starvation/ROS-mediated/chemo-therapy with an enzyme modified Fe-based MOF. Biomater Sci. 2019;7:3683–92. - PubMed
-
- Xu Q, He C, Xiao C, Chen X. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) responsive polymers for biomedical applications. Macromol Biosci. 2016;16:635–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

