CCDC65 as a new potential tumor suppressor induced by metformin inhibits activation of AKT1 via ubiquitination of ENO1 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 34335983
- PMCID: PMC8315052
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.54961
CCDC65 as a new potential tumor suppressor induced by metformin inhibits activation of AKT1 via ubiquitination of ENO1 in gastric cancer
Abstract
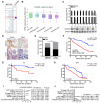
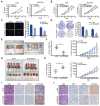
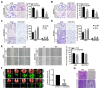
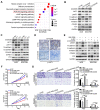
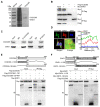
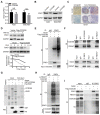
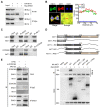
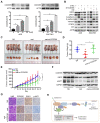
The coiled-coil domain containing protein members have been well documented for their roles in many diseases including cancers. However, the function of the coiled-coil domain containing 65 (CCDC65) remains unknown in tumorigenesis including gastric cancer. Methods: CCDC65 expression and its correlation with clinical features and prognosis of gastric cancer were analyzed in tissue. The biological role and molecular basis of CCDC65 were performed via in vitro and in vivo assays and a various of experimental methods including co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), GST-pull down and ubiquitination analysis et al. Finally, whether metformin affects the pathogenesis of gastric cancer by regulating CCDC65 and its-mediated signaling was investigated. Results: Here, we found that downregulated CCDC65 level was showed as an unfavourable factor in gastric cancer patients. Subsequently, CCDC65 or its domain (a.a. 130-484) was identified as a significant suppressor in GC growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Molecular basis showed that CCDC65 bound to ENO1, an oncogenic factor has been widely reported to promote the tumor pathogenesis, by its domain (a.a. 130-484) and further promoted ubiquitylation and degradation of ENO1 by recruiting E3 ubiquitin ligase FBXW7. The downregulated ENO1 decreased the binding with AKT1 and further inactivated AKT1, which led to the loss of cell proliferation and EMT signal. Finally, we observed that metformin, a new anti-cancer drug, can significantly induce CCDC65 to suppress ENO1-AKT1 complex-mediated cell proliferation and EMT signals and finally suppresses the malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells. Conclusion: These results firstly highlight a critical role of CCDC65 in suppressing ENO1-AKT1 pathway to reduce the progression of gastric cancer and reveals a new molecular mechanism for metformin in suppressing gastric cancer. Our present study provides a new insight into the mechanism and therapy for gastric cancer.
Keywords: AKT1; CCDC65; ENO1; Gastric cancer; Metformin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CCDC65, a Gene Knockout that leads to Early Death of Mice, acts as a potentially Novel Tumor Suppressor in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jun 27;18(10):4171-4186. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.69332. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35844805 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-enolase promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via regulating AKT signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 15;845:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.12.035. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30582908
-
Enolase1 overexpression regulates the growth of gastric cancer cells and predicts poor survival.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov;120(11):18714-18723. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29179. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31218757
-
Functional significance and therapeutic implication of ring-type E3 ligases in colorectal cancer.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 11;37(2):148-159. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.313. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28925398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ENO1 and its targeted therapy in tumors.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 14;22(1):1025. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05847-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39543641 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity to boost cancer immunotherapy.Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Apr;20(4):318-340. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-00980-8. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36823234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCDC25 suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by LATS1/YAP-mediated regulation of the hippo pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Apr 3;24(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03318-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38570766 Free PMC article.
-
Role of FBXW7 expression in gastric cancer: Meta‑analysis and bioinformatics analysis.Oncol Lett. 2023 Mar 24;25(5):184. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13770. eCollection 2023 May. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37113395 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of ag85a/b DNA vaccine conferred immunotherapy and recovery from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced injury.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 May;11(5):e854. doi: 10.1002/iid3.854. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37249284 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell dissection reveals promotive role of ENO1 in leukemia stem cell self-renewal and chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Oct 8;15(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03969-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39380054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;0:1–41. - PubMed
-
- Russo AE, Strong VE. Gastric cancer etiology and management in asia and the west. Annu Rev Med. 2019;70:353–367. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Zhang JJ, Wang L, Zhou ZM, Xu M, Li JM. et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel sperm tail protein, nyd-sp28. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18:1119–1125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

