Coronary Artery Disease: Association Study of 5 Loci with Angiographic Indices of Disease Severity
- PMID: 34336004
- PMCID: PMC8292076
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5522539
Coronary Artery Disease: Association Study of 5 Loci with Angiographic Indices of Disease Severity
Abstract
Background: Different common gene variants were related to coronary artery disease (CAD) in many studies. Yet, the relation of these loci to the severity of CAD is not completely elucidated.
Methods: We enrolled 520 subjects (315 CAD cases and 205 controls). CAD presence and extension were assessed by coronary angiography (CAG). Genotyping of five SNPs (namely, rs2230806 (1051G > A) in ABCA1 on chromosome 9, rs2075291 (553G > T) in ApoA5 on chromosome 11, rs320 in LPL on chromosome 8 intron (T → G at position 481), rs10757278 (c.22114477A > G), and rs2383206 (c.22115026 A > G) on chromosome 9p21 locus) was performed by allele-specific PCR. The degree and site of arterial lesions were used to classify patients, tested for association with CAD severity, and related to allele dosage.
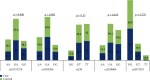
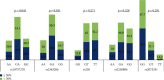
Results: The polymorphisms rs2383206 and rs10757278 showed significant associations with 2- and 3-vessel coronary disease (p =0.003 and 0.006, respectively). The homozygous GG genotypes of rs10757278 was associated with higher frequency of left anterior descending (LAD), right coronary artery (RCA) and left circumflex (LCX) diseases (p =0.002, 0.016 and 0.002, respectively). The GG genotypes of rs2383206 were found in higher percentage in patients with left main (LM) trunk and left circumflex (LCX) diseases (p = 0.013 and 0.002, respectively).
Conclusion: SNPs rs10757278 and rs2383206 allele dosage could predict CAD severity in the Saudi Arab population.
Copyright © 2021 Neda M. Bogari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest concerning this article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous