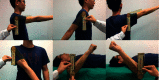
Rehabilitation of An Analgesic Bracelet Based on Wrist-Ankle Acupuncture in Patients with Rotator Cuff Injury: A Randomized Trial
- PMID: 34336070
- PMCID: PMC8292086
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9946548
Rehabilitation of An Analgesic Bracelet Based on Wrist-Ankle Acupuncture in Patients with Rotator Cuff Injury: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (C-TENS) in the rehabilitation of rotator cuff injury.
Methods: A total of 60 patients diagnosed with mild to moderate rotator cuff injury were randomly divided into the control group and test group. Both groups received conventional rehabilitation treatment including physical therapy, joint mobilization, interventional therapy, and family recovery training. The test group additionally received TENS treatment on the upper area 4 or 5 of the wrist, based on the wrist-ankle acupuncture (WAA) theory. The results of the visual analogue scale (VAS), shoulder range of motion (ROM), and Constant-Murley score (CMs) were collected before and after the 1st treatment and after the 5th treatment. The differences of those indicators between the two groups were analyzed statistically.
Results: The VAS scores of measurement points after treatment were all improved compared with those at baseline. There was a significant difference between the two groups after the 1st and the 5th treatment (p < 0.05), and the improvements in the test group were better than those in the control group. The ROM of flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, and external rotation after the 1st treatment and 5th treatment in both groups were all improved compared with those at baseline. There was no significant difference between two groups. The CMs of the two groups after the 5th treatment were all improved compared with those at baseline. There was no significant difference between two groups. No adverse events occurred during the treatment.
Conclusion: Electrical stimulation on the wrist combined with conventional rehabilitation is more effective in relieving pain than the conventional rehabilitation alone. Electrical stimulation on the wrist combined with conventional rehabilitation has no obvious effect in improving shoulder joint mobility and shoulder function.
Copyright © 2021 Wenjuan Song et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Burbank K. M., Herbert Stevenson J., Czarnecki G. R., Dorfman J. Chronic shoulder pain: part I. evaluation and diagnosis. American Family Physician. 2008;77(4):453–460. - PubMed
-
- Wilk K. E., Macrina L. C., Yenchak A. J., Cain E. L., Andrews J. R. Surgical repair and rehabilitation of a combined 330° capsulolabral lesion and partial-thickness rotator cuff tear in a professional quarterback: a case report. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 2013;43(3):142–153. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2013.3726. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elboim-Gabyzon M., Andrawus Najjar S., Shtarker H. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) on acute postoperative pain intensity and mobility after hip fracture: a double-blinded, randomized trial. Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2019;14:1841–1850. doi: 10.2147/cia.s203658. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou M., Li F., Lu W., Wu J., Pei S. Efficiency of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and transcutaneous nerve stimulation on hemiplegic shoulder pain: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2018;99(9):1730–1739. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2018.04.020. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical