Pleural empyema secondary to nephropleural fistula in complicated pyonephrosis
- PMID: 34336076
- PMCID: PMC8318834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.06.051
Pleural empyema secondary to nephropleural fistula in complicated pyonephrosis
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing patient consent statements in previously published articles.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Feb 24;18(5):2056. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.01.086. eCollection 2023 May. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37069954 Free PMC article.
Abstract
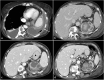
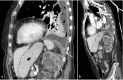
Pleural empyema of extra pulmonary origin is uncommon and empyema secondary to a fistula between the urinary tract and thorax is extremely rare. We report a case of nephropleural fistula causing massive pleural empyema in a 64-year-old woman with a long history of urological problems, including nephrolitiasis and urinary tract infection. She was admitted with sepsis, fever, chills, tachypnea, productive cough and pyuria. At clinical examination, breath sounds were reduced over the left hemithorax. CT revealed a fistulous connection from the upper left calyceal group and the pleural space. Drainage of thoracic and perinephric collection was carried out, but nephrectomy and pleural decortication were required due to haemopurulent urine and decreased hemoglobin levels during the hospitalization. This case demonstrates the unusual and prolonged evolution of an obstructive hydroureteronephrosis complicated by pyonephrosis, culminating in retroperitoneal abscess that fistulized into the pleural space, leading to empyema.
Keywords: Abscess; Computed Tomography; Nephropleural fistula; Pleural empyema; Pyonephrosis; Thoracic empyema.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

