Molecular Dysfunctions of Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Contacts in Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 34336087
- PMCID: PMC8321742
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2424509
Molecular Dysfunctions of Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Contacts in Atherosclerosis
Abstract
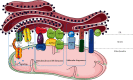
Atherosclerosis is a chronic lipid-driven inflammatory disease that results in the formation of lipid-rich and immune cell-rich plaques in the arterial wall, which has high morbidity and mortality in the world. The mechanism of atherosclerosis is still unclear now. Potential hypotheses involved in atherosclerosis are chronic inflammation theory, lipid percolation theory, mononuclear-macrophage theory, endothelial cell (EC) injury theory, and smooth muscle cell (SMC) mutation theory. Changes of phospholipids, glucose, critical proteins, etc. on mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) can cause the progress of atherosclerosis. This review describes the structural and functional interaction between mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and explains the role of critical molecules in the structure of MAM during atherosclerosis.
Copyright © 2021 Xiaojiao Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no commercial or financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The perspective of modern transplant science - transplant arteriosclerosis: inspiration derived from mitochondria associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane dysfunction in arterial diseases.Int J Surg. 2025 May 1;111(5):3430-3440. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002362. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 40146783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Where the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondrion tie the knot: the mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM).Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1833(1):213-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.04.013. Epub 2012 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22575682 Review.
-
Communications between Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum in the Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis.Cells. 2021 Aug 25;10(9):2195. doi: 10.3390/cells10092195. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highlighting the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria connection: Focus on Mitofusin 2.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Feb;128:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29309902 Review.
-
The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane-Induced Insulin Resistance.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Nov 23;11:592129. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.592129. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33329397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Contacts: A Potential Therapy Target for Cardiovascular Remodeling-Associated Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 10;9:774989. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.774989. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34858991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Insights from the Theory of General Pathological Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7910. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097910. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between Complement C1q A Chain (C1QA) and Macrophages in the Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis.Iran J Public Health. 2024 Jul;53(7):1517-1527. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v53i7.16046. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39086409 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Framework of Mouse Endothelial Cell Dysfunction during Inflammation: A Proteomics Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 29;23(15):8399. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158399. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955534 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine and its derivatives: mechanisms of action in myocardial vascular endothelial injury - a review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 4;16:1543697. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1543697. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40103596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

