Virulence of Trypanosoma cruzi Strains Is Related to the Differential Expression of Innate Immune Receptors in the Heart
- PMID: 34336720
- PMCID: PMC8321543
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.696719
Virulence of Trypanosoma cruzi Strains Is Related to the Differential Expression of Innate Immune Receptors in the Heart
Abstract
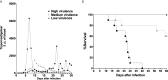
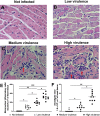
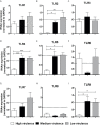
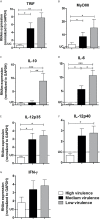
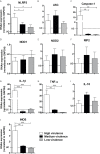
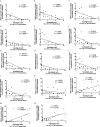
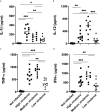
Resistance or susceptibility to T. cruzi infection is dependent on the host immunological profile. Innate immune receptors, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs/TLR2, TLR4, TLR7, and TLR9) and Nod-like receptors (NLRs/NOD1 and NLRP3 inflammasome) are involved with the resistance against acute experimental T. cruzi infection. Here, we evaluated the impact of T. cruzi virulence on the expression of innate immune receptors and its products in mice. For that, we used six T. cruzi strains/isolates that showed low (AM64/TcIV and 3253/Tc-V), medium (PL1.10.14/TcIII and CL/TcVI), or high (Colombian/Tc-I and Y/TcII) virulence and pathogenicity to the vertebrate host and belonging to the six discrete typing units (DTUs)-TcI to TcVI. Parasitemia, mortality, and myocarditis were evaluated and correlated to the expression of TLRs, NLRs, adapter molecules, cytokines, and iNOS in myocardium by real time PCR. Cytokines (IL-1β, IL-12, TNF-α, and IFN-γ) were quantified in sera 15 days after infection. Our data indicate that high virulent strains of T. cruzi, which generate high parasitemia, severe myocarditis, and 100% mortality in infected mice, inhibit the expression of TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, TRIF, and Myd88 transcripts, leading to a low IL-12 production, when compared to medium and low virulent T. cruzi strains. On the other hand, the high virulent T. cruzi strains induce the upregulation of NLRP3, caspase-1, IL-1β, TNF-α, and iNOS mRNA in heart muscle, compared to low and medium virulent strains, which may contribute to myocarditis and death. Moreover, high virulent strains induce higher levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in sera compared to less virulent parasites. Altogether the data indicate that differential TLR and NLR expression in heart muscle is correlated with virulence and pathogenicity of T cruzi strains. A better knowledge of the immunological mechanisms involved in resistance to T. cruzi infection is important to understand the natural history of Chagas disease, can lead to identification of immunological markers and/or to serve as a basis for alternative therapies.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; Nod-like receptor; Toll-like receptor; Trypanosoma cruzi; innate immune receptors; mice; virulence.
Copyright © 2021 Queiroga, Pereira, Silva, Andrade, Araújo Júnior, Brito, Galvão, Câmara, Nascimento and Guedes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aliberti J. C., Cardoso M. A., Martins G. A., Gazzinelli R. T., Vieira L. Q., Silva J. S. (1996). Interleukin-12 Mediates Resistance to Trypanosoma Cruzi in Mice and Is Produced by Murine Macrophages in Response to Live Trypomastigotes. Infect Immun. 64 (6), 1961–1967. 10.1128/iai.64.6.1961-1967.1996 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahia-Oliveira L. M., Gomes J. A., Rocha M. O., Moreira M. C., Lemos E. M., Luz Z. M., et al. (1998). IFN-Gamma in Human Chagas’ Disease: Protection or Pathology? Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. = Rev. Bras. pesquisas Med e biologicas/Sociedade Bras. Biofisica [et al.] 31 (1), 127–131. 10.1590/s0100-879x1998000100017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

