Characterization of an Enterococcus faecalis Bacteriophage vB_EfaM_LG1 and Its Synergistic Effect With Antibiotic
- PMID: 34336721
- PMCID: PMC8322680
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.698807
Characterization of an Enterococcus faecalis Bacteriophage vB_EfaM_LG1 and Its Synergistic Effect With Antibiotic
Abstract
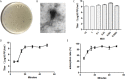
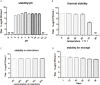
Enterococcus faecalis is a Gram-positive opportunistic pathogen that could cause pneumonia and bacteremia in stroke patients. The development of antibiotic resistance in hospital-associated E. faecalis is a formidable public health threat. Bacteriophage therapy is a renewed solution to treat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. However, bacteria can acquire phage resistance quite quickly, which is a significant barrier to phage therapy. Here, we characterized a lytic E. faecalis bacteriophage Vb_EfaM_LG1 with lytic activity. Its genome did not contain antibiotic resistance or virulence genes. Vb_EfaM_LG1 effectively inhibits E. faecalis growth for a short period, and phage resistance developed within hours. However, the combination of antibiotics and phage has a tremendous synergistic effect against E. faecalis, prevents the development of phage resistance, and disrupts the biofilm efficiently. Our results show that the phage-antibiotic combination has better killing efficiency against E. faecalis.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecalis; antibiotic resistance; bacteriophage; phage therapy; phage-antibiotic combination.
Copyright © 2021 Song, Wu, Hu, Luo and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

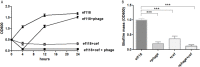
Similar articles
-
Novel strategies for vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis biofilm control: bacteriophage (vB_EfaS_ZC1), propolis, and their combined effects in an ex vivo endodontic model.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2025 Apr 13;24(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12941-025-00790-y. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2025. PMID: 40223105 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Lytic Enterococcus Phage vB_Efs8_KEN04 against Clinical Isolates of Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis in Kenya.Viruses. 2024 Aug 9;16(8):1275. doi: 10.3390/v16081275. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205249 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of a newly isolated bacteriophage against multi-drug resistant Enterococcus faecalis infections: in vitro and in vivo characterization.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Feb 20;25(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03785-z. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39979834 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Phage Therapy in the Context of Enterococcus faecalis and Its Associated Diseases.Viruses. 2019 Apr 20;11(4):366. doi: 10.3390/v11040366. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31010053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage therapy: A renewed approach against oral diseases caused by Enterococcus faecalis infections.Microb Pathog. 2024 Apr;189:106574. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106574. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38354990 Review.
Cited by
-
The Combination of Phage Therapy and β-Lactam Antibiotics for the Effective Treatment of Enterococcus faecalis Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):11. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010011. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795870 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro resensitization of multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium and E. faecalis through phage-antibiotic synergy.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Feb 13;69(2):e0074024. doi: 10.1128/aac.00740-24. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39699213 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of a phage cocktail in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae pulmonary infection in mice.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Mar 17;25(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03851-6. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40098144 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies and mechanisms targeting Enterococcus faecalis biofilms associated with endodontic infections: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 18;14:1433313. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1433313. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39091674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of vB_PreP_EPr2, a Lytic Bacteriophage of Pan-Drug Resistant Providencia rettgeri.Viruses. 2022 Mar 29;14(4):708. doi: 10.3390/v14040708. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banla I. L., Kommineni S., Hayward M., Rodrigues M., Palmer K. L., Salzman N. H., et al. . (2018). Modulators of Enterococcus Faecalis Cell Envelope Integrity and Antimicrobial Resistance Influence Stable Colonization of the Mammalian Gastrointestinal Tract. Infect. Immun. 86 (1), e00381-17. 10.1128/IAI.00381-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bao J., Wu N., Zeng Y., Chen L., Li L., Yang L., et al. . (2020). Non-Active Antibiotic and Bacteriophage Synergism to Successfully Treat Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection Caused by Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 9, 771–774. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1747950 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

