Cancer-Associated Fibroblast (CAF) Heterogeneity and Targeting Therapy of CAFs in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 34336821
- PMCID: PMC8319605
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.655152
Cancer-Associated Fibroblast (CAF) Heterogeneity and Targeting Therapy of CAFs in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
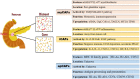
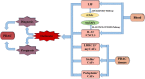
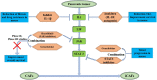
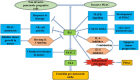
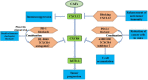
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly lethal disease that typically features a dramatic desmoplastic reaction, especially fibroblasts. The roles of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in PDAC have received more attention in recent years. As increasing evidence suggests the heterogeneity of CAFs in PDAC, different CAF subtypes have been shown to support tumor growth, while others suppress cancer proliferation. Myofibrotic CAFs (myCAFs) show alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) high interleukin-6 (IL-6) low myofibroblastic features, are activated by direct contact with tumor cells, and are located in the periglandular region. Inflammatory CAFs (iCAFs) show α-SMA low IL-6 high inflammatory features, are activated by paracrine factors secreted from tumor cells, and are located away from cancer cells. Antigen-presenting CAFs (apCAFs) show major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II) family genes that are highly expressed. CAFs have also been gradually explored as diagnostic and prognostic markers in pancreatic cancer. Targeted therapy of CAFs in PDAC has gradually attracted attention. With the deepening of related studies, some meaningful positive and negative results have surfaced, and CAFs may be the key to unlocking the door to pancreatic cancer treatment. Our review summarizes recent advances in the heterogeneity, function, and markers of CAFs in pancreatic cancer, as well as research and treatment targeting CAFs in pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: cancer-associated fibroblasts; diagnosis; hallmark; heterogeneity; pancreatic cancer; prognosis; therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Geng, Chen, Zhao, Hu, Yang, Li, Cheng, Zhao, Zhang, Li and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medical Biology of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Cancer.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;12(8):1044. doi: 10.3390/biology12081044. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37626931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome Landscape of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Human PDAC.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(20):e2415196. doi: 10.1002/advs.202415196. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40019403 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Diversity Shapes Tumor Metabolism in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;15(1):61. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010061. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAFs-Associated Genes (CAFGs) in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and Novel Therapeutic Strategy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 30;25(11):6003. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116003. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inter- and intra-tumoural heterogeneity in cancer-associated fibroblasts of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Pathol. 2019 May;248(1):51-65. doi: 10.1002/path.5224. Epub 2019 Feb 22. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30575030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Cell Biology of Metastatic Invasion in Pancreatic Cancer: Updates and Mechanistic Insights.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 6;15(7):2169. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072169. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-Educated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Facilitate Malignant Progression of Ovarian Cancer Cells via the NF-kB/IL-6/JAK2 Signal Transduction.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;67(1):317-328. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01055-3. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38305842
-
Combination of anlotinib with immunotherapy enhanced both anti-angiogenesis and immune response in high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 7;16:1539616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1539616. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40260248 Free PMC article.
-
KRT7 promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis by remodeling the extracellular matrix niche through FGF2-fibroblast crosstalk.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 26;15(1):6951. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84129-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40011455 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast subtypes modulate the tumor-immune microenvironment and are associated with skin cancer malignancy.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 8;15(1):9678. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53908-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39516494 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

