Giardia duodenalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Mouse Macrophages via TLR9-Mediated p38 and ERK Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 34336841
- PMCID: PMC8319647
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.694675
Giardia duodenalis Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Mouse Macrophages via TLR9-Mediated p38 and ERK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
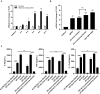
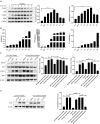
Giardia duodenalis, also known as Giardia lamblia or Giardia intestinalis, is an important opportunistic, pathogenic, zoonotic, protozoan parasite that infects the small intestines of humans and animals, causing giardiasis. Several studies have demonstrated that innate immunity-associated Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are critical for the elimination of G. duodenalis; however, whether TLR9 has a role in innate immune responses against Giardia infection remains unknown. In the present study, various methods, including reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunofluorescence, inhibitor assays, and small-interfering RNA interference, were utilized to probe the role of TLR9 in mouse macrophage-mediated defenses against G. lamblia virus (GLV)-free or GLV-containing Giardia trophozoites. The results revealed that in G. duodenalis-stimulated mouse macrophages, the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and IL-12 p40, was enhanced, concomitant with the significant activation of TLR9, whereas silencing TLR9 attenuated the host inflammatory response. Notably, the presence of GLV exacerbated the secretion of host proinflammatory cytokines. Moreover, G. duodenalis stimulation activated multiple signaling pathways, including the nuclear factor κB p65 (NF-κB p65), p38, ERK, and AKT pathways, the latter three in a TLR9-dependent manner. Additionally, inhibiting the p38 or ERK pathway downregulated the G. duodenalis-induced inflammatory response, whereas AKT inhibition aggravated this process. Taken together, these results indicated that G. duodenalis may induce the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by activating the p38 and ERK signaling pathways in a TLR9-dependent manner in mouse macrophages. Our in vitro findings on the mechanism underlying the TLR9-mediated host inflammatory response may help establish the foundation for an in-depth investigation of the role of TLR9 in the pathogenicity of G. duodenalis.
Keywords: ERK; Giardia duodenalis; TLR9; cytokines; p38.
Copyright © 2021 Pu, Li, Cao, Yue, Zhao, Wang, Li, Zhang, Zhang, Zhao, Liang and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Giardia duodenalis extracellular vesicles regulate the proinflammatory immune response in mouse macrophages in vitro via the MAPK, AKT and NF-κB pathways.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Jul 8;14(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04865-5. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34238339 Free PMC article.
-
RAGE-mediated intestinal pro-inflammatory responses triggered by Giardia duodenalis.Acta Trop. 2025 Feb;262:107529. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2025.107529. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Acta Trop. 2025. PMID: 39848554
-
TLR2-/- Mice Display Decreased Severity of Giardiasis via Enhanced Proinflammatory Cytokines Production Dependent on AKT Signal Pathway.Front Immunol. 2017 Sep 20;8:1186. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01186. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28979269 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptions of Host Immunity and Inflammation by Giardia Duodenalis: Potential Consequences for Co-Infections in the Gastro-Intestinal Tract.Pathogens. 2015 Nov 10;4(4):764-92. doi: 10.3390/pathogens4040764. Pathogens. 2015. PMID: 26569316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Proteomics to the Study of the Therapeutics and Pathogenicity of Giardia duodenalis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;12(11):2744. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112744. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Matryoshka: Addressing the Relationship between Pathogenic Flagellated Protozoans and Their RNA Viral Endosymbionts (Family Totiviridae).Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 17;11(7):321. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11070321. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39058005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential activity of Ferula macrecolea essential oil for treating Giardia lamblia infection through modulating electrolytes and suppressing NF-κB p65 pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 18;16:1542425. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542425. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40041488 Free PMC article.
-
A parasite odyssey: An RNA virus concealed in Toxoplasma gondii.Virus Evol. 2024 May 11;10(1):veae040. doi: 10.1093/ve/veae040. eCollection 2024. Virus Evol. 2024. PMID: 38817668 Free PMC article.
-
Trophozoite fitness dictates the intestinal epithelial cell response to Giardia intestinalis infection.PLoS Pathog. 2023 May 4;19(5):e1011372. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011372. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37141303 Free PMC article.
-
The Exosome-like Vesicles of Giardia Assemblages A, B, and E Are Involved in the Delivering of Distinct Small RNA from Parasite to Parasite.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 31;24(11):9559. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119559. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298511 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

