Predictors of Failed Intrauterine Balloon Tamponade in the Management of Severe Postpartum Hemorrhage
- PMID: 34336876
- PMCID: PMC8319466
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.656422
Predictors of Failed Intrauterine Balloon Tamponade in the Management of Severe Postpartum Hemorrhage
Abstract
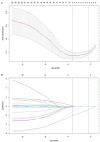
To identify the factors predicting intrauterine balloon tamponade (IUBT) failure for severe postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) after delivery, we conducted a retrospective cohort study of women who underwent IUBT for severe PPH after delivery from October 1, 2016 until September 30, 2017. The failure of IUBT was defined as the need of additional surgical procedures or uterine embolization. A total of 99,650 deliveries occurred during the study period. Among the patients, 106 cases of severe PPH were managed with IUBT, and the global success rate was 70.8% (75/106). Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was performed to select the potential risk factors predicting IUBT failure. The associated risk factors-obesity, multiple gestation, cesarean delivery, estimated blood loss (EBL), and placenta accreta spectrum (PAS)-were included in multivariate logistic models. Ultimately, these models identified multiple gestation, EBL, and PAS as independent risk factors for IUBT failure. In conclusion, IUBT is an effective method for severe PPH. The presence of factors affecting IUBT failure should be recognized early, and other modalities of management should be anticipated.
Keywords: hysterectomy; intrauterine balloon tamponade; multiple gestation; placenta accreta spectrum; postpartum hemorrhage.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Gao, Liu, Wang, He, Sun, Liu and Liao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

