Thiopurines in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. How to Optimize Thiopurines in the Biologic Era?
- PMID: 34336887
- PMCID: PMC8322650
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.681907
Thiopurines in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. How to Optimize Thiopurines in the Biologic Era?
Abstract
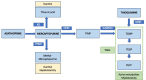
Thiopurines have been a cornerstone in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Although they have been used for more than 50 years, there are still some unsolved issues about their efficacy and, also, some safety concerns, mainly the risk of myelosuppression and life-threatening lymphoproliferative disorders. Furthermore, the development of biological therapy raises the question whether there is still a role for thiopurines in the IBD treatment algorithm. On the other hand, limited cost and wide availability make thiopurines a reasonable option in settings of limited resources and increasing prevalence of IBD. In fact, there is a growing interest in optimizing thiopurine therapy, since pharmacogenomic findings suggest that a personalized approach based on the genotyping of some molecules involved in its metabolism could be useful to prevent side effects. Polymorphisms of thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme (TPMT) that result in low enzymatic activity have been associated with an increased risk of myelotoxicity, especially in Caucasians; however, in Asians it is assumed that the variants of nudix hydrolase 15 (NUDT15) are more relevant in the development of toxicity. Age is also important, since in elderly patients the risk of complications seems to be increased. Moreover, the primo-infection of Epstein Barr virus and cytomegalovirus under thiopurine treatment has been associated with severe lymphoproliferative disorders. In addition to assessing individual characteristics that may influence thiopurines treatment outcomes, this review also discusses other strategies to optimize the therapy. Low-dose thiopurines combined with allopurinol can be used in hypermethylators and in thiopurine-related hepatotoxicity. The measurement of metabolites could be useful to assess compliance, identify patients at risk of adverse events and also facilitating the management of refractory patients. Thioguanine is also a rescue therapy in patients with toxicity related to conventional thiopurine therapy. Finally, the current indications for thiopurines in monotherapy or in combination with biologics, as well as the optimal duration of treatment, are also reviewed.
Keywords: indications; inflammatory bowel disease; optimize; pharmacogenomics; thiopurines; toxicity.
Copyright © 2021 Gargallo-Puyuelo, Laredo and Gomollón.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bermejo F, Aguas M, Chaparro M, Domènech E, Echarri A, García-Planella E, et al. Recommendations of the Spanish Working Group on Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis (GETECCU) on the use of thiopurines in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 41:205–21. 10.1016/j.gastre.2018.03.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

